Rapid response to systemic bevacizumab therapy in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
- PMID: 25289079
- PMCID: PMC4186578
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2486
Rapid response to systemic bevacizumab therapy in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
Abstract
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a primary benign disease, which is characterized by papillomatous growth in the respiratory tract. Malignant transformation occurs in only 3-5% of cases, however, local growth of the benign papillomas is interpreted as clinically malignant in a markedly higher proportion of patients. Local surgical or endoscopic interventional debulking or excision is currently the commonly selected treatment method and antiviral therapy is a potential adjuvant approach. However, the long-term management of RRP patients, who commonly require multiple procedures over numerous years, is challenging and the overall therapeutic armamentarium remains unsatisfactory. The administration of systemic bevacizumab treatment in a series of five patients with long histories of RRP, who required repeated local interventions to control papilloma growth is evaluated. Treatment with the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody bevacizumab was administered at a dose of 5 mg/kg (n=1), 10 mg/kg (n=3) or 15 mg/kg (n=1) intravenously to the five RRP patients, who were clinically classified as exhibiting progressive disease. Endoscopic evaluations were performed prior to the first infusion of bevacizumab and intermittently at variable time points during the course of therapy. Histopathological analyses were performed using pre- and post-treatment papilloma biopsies, including immunohistochemical analyses of VEGF and phosphorylated VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-2 expression. The patients received between three and 16 courses of bevacizumab (median, six courses). The first course was initiated when progression following the previous intervention was observed. An immediate response to bevacizumab treatment was demonstrated in all five RRP patients. While the cumulative number of interventions in the five patients was 18 throughout the 12 months prior to the initiation of bevacizumab treatment, only one patient required interventional treatment due to a malignant transformation during the 12 months following treatment with bevacizumab (18 vs. 1 interventions, P=0.042). Histopathological analyses revealed regressive perivascular edema and normalization of the vascular structure, however, immunohistochemical analyses of the VEGF and phosphorylated VEGFR-2 expression did not demonstrate any changes following therapy. Due to the limited number of alternative treatments, VEGF-targeted therapies may represent a promising novel strategy in the treatment of RRP, which may have the potential to modify the current treatment standards, particularly in patients with poorly accessible papilloma lesions, however, this requires further investigation in clinical trials.
Keywords: anti-angiogenesis; bevacizumab; papillomatosis.
Figures
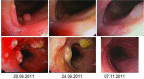
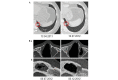
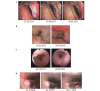
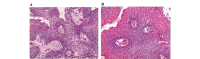
References
-
- Glikman D, Baroody FM. Images in clinical medicine. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with lung involvement. New Engl J Med. 2005;352:e22. - PubMed
-
- Derkay CS, Wiatrak B. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a review. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1236–1247. - PubMed
-
- Kimberlain DW. Current status of antiviral therapy for juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Antiviral Res. 2004;63:141–151. - PubMed
-
- Gélinas JF, Manoukian J, Côté A. Lung involvement in juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72:433–452. - PubMed
-
- Chadha NK, James A. Adjuvant antiviral therapy for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 20102010:CD005053. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
