Minimally painful local anesthetic injection for cleft lip/nasal repair in grown patients
- PMID: 25289364
- PMCID: PMC4174243
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000077
Minimally painful local anesthetic injection for cleft lip/nasal repair in grown patients
Abstract
Introduction: There has been a recent interest in injecting large body and face areas with local anesthetic in a minimally painful manner. The method includes adherence to minimal pain injection details as well feedback from the patient who counts the number of times he feels pain during the injection process. This article describes the successes and limitations of this technique as applied to primary cleft lip/nasal repair in grown patients.
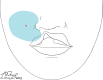
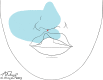
Methods: Thirty-two primary cleft lip patients were injected with local anesthesia by 3 surgeons and then underwent surgical correction of their deformity. At the beginning of the injection of the local anesthetic, patients were instructed to clearly inform the injector each and every time they felt pain during the entire injection process.
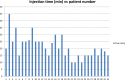
Results: The average patient felt pain only 1.6 times during the injection process. This included the first sting of the first 27-gauge needle poke. The only pain that 51% of the patients felt was that first poke of the first needle; 24% of the patients only felt pain twice during the whole injection process. The worst pain score occurred in a patient who felt pain 6 times during the injection process. Ninety-one percent of the patients felt no pain at all after the injection of the local anesthetic and did not require a top-up.
Conclusion: It is possible to successfully and reliably inject local anesthesia in a minimally painful manner for cleft lip and nasal repair in the fully grown cleft patient.
Figures








Similar articles
-
How to Minimize the Pain of Local Anesthetic Injection for Wide Awake Surgery.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Aug 4;9(8):e3730. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003730. eCollection 2021 Aug. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34367856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgeons Can Decrease the Pain of WALANT Local Anesthesia Injection if They Ask for Patient Feedback.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2025 Mar 29:22925503251327930. doi: 10.1177/22925503251327930. Online ahead of print. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2025. PMID: 40170885 Free PMC article.
-
Teaching medical students and residents how to inject local anesthesia almost painlessly.Can J Plast Surg. 2012 Fall;20(3):169-72. doi: 10.1177/229255031202000315. Can J Plast Surg. 2012. PMID: 23997583 Free PMC article.
-
Minimizing the pain of local anesthesia injection.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013 Sep;132(3):675-684. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31829ad1e2. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013. PMID: 23985640 Review.
-
Finer Needles Reduce Pain Associated With Injection of Local Anesthetic Using a Minimal Insertion Injection Technique.Dermatol Surg. 2018 Feb;44(2):204-208. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001279. Dermatol Surg. 2018. PMID: 29016543 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
WALANT Decreases Costs of Surgery to Increase Access and Help Alleviate Poverty in East Africa.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Mar 21;13(3):e6572. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006572. eCollection 2025 Mar. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40125460 Free PMC article.
-
How to Minimize the Pain of Local Anesthetic Injection for Wide Awake Surgery.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Aug 4;9(8):e3730. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003730. eCollection 2021 Aug. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34367856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimal Pain Local Anesthetic Injection with Blunt Tipped Cannula for Wide Awake Upper Blepharoplasty.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017 May 4;5(5):e1310. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001310. eCollection 2017 May. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017. PMID: 28607847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lalonde DH. “Hole-in-one” local anesthesia for wide-awake carpal tunnel surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126:1642–1644. - PubMed
-
- Strazar AR, Leynes PG, Lalonde DH. Minimizing the pain of local anesthesia injection. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132:675–684. - PubMed
-
- Burk RW, 3rd, Guzman-Stein G, Vasconez LO. Lidocaine and epinephrine levels in tumescent technique liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;97:1379–1384. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
