Cell turnover and detritus production in marine sponges from tropical and temperate benthic ecosystems
- PMID: 25289641
- PMCID: PMC4188633
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109486
Cell turnover and detritus production in marine sponges from tropical and temperate benthic ecosystems
Abstract
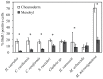
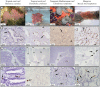
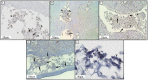
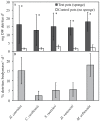
This study describes in vivo cell turnover (the balance between cell proliferation and cell loss) in eight marine sponge species from tropical coral reef, mangrove and temperate Mediterranean reef ecosystems. Cell proliferation was determined through the incorporation of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) and measuring the percentage of BrdU-positive cells after 6 h of continuous labeling (10 h for Chondrosia reniformis). Apoptosis was identified using an antibody against active caspase-3. Cell loss through shedding was studied quantitatively by collecting and weighing sponge-expelled detritus and qualitatively by light microscopy of sponge tissue and detritus. All species investigated displayed substantial cell proliferation, predominantly in the choanoderm, but also in the mesohyl. The majority of coral reef species (five) showed between 16.1±15.9% and 19.0±2.0% choanocyte proliferation (mean±SD) after 6 h and the Mediterranean species, C. reniformis, showed 16.6±3.2% after 10 h BrdU-labeling. Monanchora arbuscula showed lower choanocyte proliferation (8.1±3.7%), whereas the mangrove species Mycale microsigmatosa showed relatively higher levels of choanocyte proliferation (70.5±6.6%). Choanocyte proliferation in Haliclona vansoesti was variable (2.8-73.1%). Apoptosis was negligible and not the primary mechanism of cell loss involved in cell turnover. All species investigated produced significant amounts of detritus (2.5-18% detritus bodyweight(-1)·d(-1)) and cell shedding was observed in seven out of eight species. The amount of shed cells observed in histological sections may be related to differences in residence time of detritus within canals. Detritus production could not be directly linked to cell shedding due to the degraded nature of expelled cellular debris. We have demonstrated that under steady-state conditions, cell turnover through cell proliferation and cell shedding are common processes to maintain tissue homeostasis in a variety of sponge species from different ecosystems. Cell turnover is hypothesized to be the main underlying mechanism producing sponge-derived detritus, a major trophic resource transferred through sponges in benthic ecosystems, such as coral reefs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Richter C, Wunsch M, Rasheed M, Kötter I, Badran M (2001) Endoscopic exploration of Red Sea coral reefs reveals dense populations of cavity-dwelling sponges. Nature 413: 726–730. - PubMed
-
- De Goeij JM, van den Berg H, van Oostveen MM, Epping EHG, Van Duyl FC (2008) Major bulk dissolved organic carbon (DOC) removal by encrusting coral reef cavity sponges. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 357: 139–151.
-
- De Goeij JM, van Oevelen D, Vermeij MJA, Osinga R, Middelburg JJ, et al. (2013) Surviving in a marine desert: The sponge loop retains resources within coral reefs. Science 342: 108–110. - PubMed
-
- Yahel G, Sharp J, Marie D, Hase C, Genin A (2003) In situ feeding and element removal in the symbiont-bearing sponge Theonella swinhoei: Bulk DOC is the major source for carbon. Limnol Oceanogr 48: 141–149.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

