Locational diversity of alpha satellite DNA and intergeneric hybridization aspects in the Nomascus and Hylobates genera of small apes
- PMID: 25290445
- PMCID: PMC4188616
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109151
Locational diversity of alpha satellite DNA and intergeneric hybridization aspects in the Nomascus and Hylobates genera of small apes
Abstract
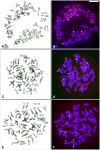
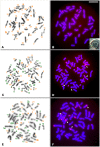
Recently, we discovered that alpha satellite DNA has unique and genus-specific localizations on the chromosomes of small apes. This study describes the details of alpha satellite localization in the genera Nomascus and Hylobates and explores their usefulness in distinguishing parental genome sets in hybrids between these genera. Fluorescence in situ hybridization was used to establish diagnostic criteria of alpha satellite DNA markers in discriminating small ape genomes. In particular we established the genus specificity of alpha satellite distribution in three species of light-cheeked gibbons (Nomascus leucogenys, N. siki, and N. gabriellae) in comparison to that of Hylobates lar. Then we determined the localization of alpha satellite DNA in a hybrid individual which resulted from a cross between these two genera. In Nomascus the alpha satellite DNA blocks were located at the centromere, telomere, and four interstitial regions. In Hylobates detectable amounts of alpha satellite DNA were seen only at centromeric regions. The differences in alpha satellite DNA locations between Nomascus and Hylobates allowed us to easily distinguish the parental chromosomal sets in the genome of intergeneric hybrid individuals found in Thai and Japanese zoos. Our study illustrates how molecular cytogenetic markers can serve as diagnostic tools to identify the origin of individuals. These molecular tools can aid zoos, captive breeding programs and conservation efforts in managing small apes species. Discovering more information on alpha satellite distribution is also an opportunity to examine phylogenetic and evolutionary questions that are still controversial in small apes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A most distant intergeneric hybrid offspring (Larcon) of lesser apes, Nomascus leucogenys and Hylobates lar.Hum Genet. 2007 Dec;122(5):477-83. doi: 10.1007/s00439-007-0425-0. Epub 2007 Aug 24. Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17717705
-
In situ hybridization analysis of gibbon chromosomes suggests that amplification of alpha satellite DNA in the telomere region is confined to two of the four genera.Genome. 2012 Nov;55(11):809-12. doi: 10.1139/gen-2012-0123. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Genome. 2012. PMID: 23199575
-
Tracking the complex flow of chromosome rearrangements from the Hominoidea Ancestor to extant Hylobates and Nomascus Gibbons by high-resolution synteny mapping.Genome Res. 2008 Sep;18(9):1530-7. doi: 10.1101/gr.078295.108. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18552313 Free PMC article.
-
An apparently acentric marker chromosome originating from 9p with a functional centromere without detectable alpha and beta satellite sequences.Am J Med Genet. 1997 Sep 5;71(4):436-42. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970905)71:4<436::aid-ajmg13>3.0.co;2-h. Am J Med Genet. 1997. PMID: 9286452 Review.
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization to chromosomes as a tool to understand human and primate genome evolution.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005;108(1-3):139-60. doi: 10.1159/000080811. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 15545725 Review.
Cited by
-
Satellite DNA in Neotropical Deer Species.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;12(1):123. doi: 10.3390/genes12010123. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33478071 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Rapid Karyotype Evolution in Mammals.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 31;15(1):62. doi: 10.3390/genes15010062. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38254952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Satellite DNAs in Squirrel Monkeys genus Saimiri (Cebidae, Platyrrhini).Sci Rep. 2020 May 8;10(1):7783. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64620-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32385398 Free PMC article.
-
Application of multicolor banding combined with heterochromatic and locus-specific probes identify evolutionary conserved breakpoints in Hylobates pileatus.Mol Cytogenet. 2016 Feb 17;9:17. doi: 10.1186/s13039-016-0228-x. eCollection 2016. Mol Cytogenet. 2016. PMID: 26893612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold ML, Meyer A (2006) Natural hybridization in primates: one evolutionary mechanism. Zoology 109: 261–276. - PubMed
-
- Myers RH, Shafer DA (1979) Hybrid ape offspring of a mating of gibbon and siamang. Science 205: 308–310. - PubMed
-
- Marshall J, Sugardjito J (1986) Gibbon systematics. In: Swindler DR, Erwin J, editors. Comparative primate biology, vol. 1, systematics, evolution, and anatomy. New York: Alan R. Liss. pp. 137–185.
-
- Jolly CJ, Wooley-Barker T, Beyene S, Disotell TR, Phillips-Conroy JE (1997) Intergeneric hybrid baboons. Int J Primat 18: 597–627.
-
- Hirai H, Hirai Y, Domae H, Kirihara Y (2007) A most distant intergeneric hybrid offspring (Larcon) of lesser apes, Nomascus leucogenys and Hylobates lar. Human Genet 122: 477–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

