Blood lipids and the incidence of atrial fibrillation: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and the Framingham Heart Study
- PMID: 25292185
- PMCID: PMC4323837
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001211
Blood lipids and the incidence of atrial fibrillation: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and the Framingham Heart Study
Abstract
Background: Dyslipidemia is a major contributor to the development of atherosclerosis and coronary disease. Its role in the etiology of atrial fibrillation (AF) is uncertain.
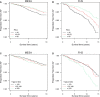
Methods and results: We studied 7142 men and women from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Framingham Heart Study who did not have prevalent AF at baseline and were not on lipid-lowering medications. Total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides were measured using standard procedures. Incident AF during follow-up was identified from hospital discharge codes; review of medical charts; study electrocardiograms; and, in MESA only, Medicare claims. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals of AF by clinical categories of blood lipids in each cohort. Study-specific results were meta-analyzed using inverse of variance weighting. During 9.6 years of mean follow-up, 480 AF cases were identified. In a combined analysis of multivariable-adjusted results from both cohorts, high levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol were associated with lower AF risk (hazard ratio 0.64, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.87 in those with levels ≥60 mg/dL versus <40 mg/dL), whereas high triglycerides were associated with higher risk of AF (hazard ratio 1.60, 95% CI 1.25 to 2.05 in those with levels ≥200 mg/dL versus <150 mg/dL). Total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were not associated with the risk of AF.
Conclusion: In these 2 community-based cohorts, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides but not low-density lipoprotein cholesterol or total cholesterol were associated with the risk of AF, accounting for other cardiometabolic risk factors.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cholesterol; epidemiology; lipids; risk factors.
© 2014 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


References
-
- LaRosa JC, He J, Vupputuri S. Effect of statins on risk of coronary disease: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 1999; 282:2340-2346. - PubMed
-
- Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, Kors JA, van Rooij FJ, Lip GY, Witteman JC. Subclinical atherosclerosis and risk of atrial fibrillation: the Rotterdam Study. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167:382-387. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe H, Tanabe N, Yagihara N, Watanabe T, Aizawa Y, Kodama M. Association between lipid profile and risk of atrial fibrillation. Circ J. 2011; 75:2767-2774. - PubMed
-
- Lopez FL, Agarwal SK, MacLehose RF, Soliman EZ, Sharrett AR, Huxley RR, Konety S, Ballantyne CM, Alonso A. Blood lipid levels, lipid‐lowering medications, and the incidence of atrial fibrillation: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012; 5:155-162. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1RC1HL101056/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 6R01NS17950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01HL102214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL101056/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

