CD4+ invariant natural killer T cells protect from murine GVHD lethality through expansion of donor CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells
- PMID: 25293774
- PMCID: PMC4239338
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-576017
CD4+ invariant natural killer T cells protect from murine GVHD lethality through expansion of donor CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells
Abstract
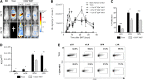
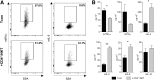
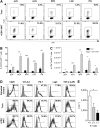
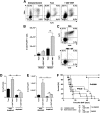
Dysregulated donor T cells lead to destruction of host tissues resulting in graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). We investigated the impact of highly purified (>95%) donor CD4(+) invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells on GVHD in a murine model of allogeneic HCT. We found that low doses of adoptively transferred donor CD4(+) iNKT cells protect from GVHD morbidity and mortality through an expansion of donor CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs). These Tregs express high levels of the Ikaros transcription factor Helios and expand from the Treg pool of the donor graft. Furthermore, CD4(+) iNKT cells preserve T-cell-mediated graft-versus-tumor effects. Our studies reveal new aspects of the cellular interplay between iNKT cells and Tregs in the context of tolerance induction after allogeneic HCT and set the stage for clinical translation.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


References
-
- Ferrara JL, Deeg HJ. Graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(10):667–674. - PubMed
-
- Edinger M, Hoffmann P, Ermann J, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells preserve graft-versus-tumor activity while inhibiting graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Nat Med. 2003;9(9):1144–1150. - PubMed
-
- Di Ianni M, Falzetti F, Carotti A, et al. Tregs prevent GVHD and promote immune reconstitution in HLA-haploidentical transplantation. Blood. 2011;117(14):3921–3928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

