Optineurin is an autophagy receptor for damaged mitochondria in parkin-mediated mitophagy that is disrupted by an ALS-linked mutation
- PMID: 25294927
- PMCID: PMC4210283
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1405752111
Optineurin is an autophagy receptor for damaged mitochondria in parkin-mediated mitophagy that is disrupted by an ALS-linked mutation
Abstract
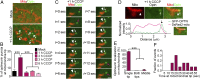
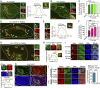
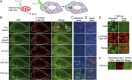
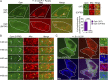
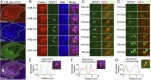
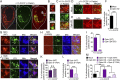
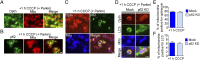
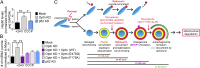
Mitophagy is a cellular quality control pathway in which the E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin targets damaged mitochondria for degradation by autophagosomes. We examined the role of optineurin in mitophagy, as mutations in optineurin are causative for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and glaucoma, diseases in which mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated. Using live cell imaging, we demonstrate the parkin-dependent recruitment of optineurin to mitochondria damaged by depolarization or reactive oxygen species. Parkin's E3 ubiquitin ligase activity is required to ubiquitinate outer mitochondrial membrane proteins, allowing optineurin to stably associate with ubiquitinated mitochondria via its ubiquitin binding domain; in the absence of parkin, optineurin transiently localizes to damaged mitochondrial tips. Following optineurin recruitment, the omegasome protein double FYVE-containing protein 1 (DFCP1) transiently localizes to damaged mitochondria to initialize autophagosome formation and the recruitment of microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3). Optineurin then induces autophagosome formation around damaged mitochondria via its LC3 interaction region (LIR) domain. Depletion of endogenous optineurin inhibits LC3 recruitment to mitochondria and inhibits mitochondrial degradation. These defects are rescued by expression of siRNA-resistant wild-type optineurin, but not by an ALS-associated mutant in the ubiquitin binding domain (E478G), or by optineurin with a mutation in the LIR domain. Optineurin and p62/SQSTM1 are independently recruited to separate domains on damaged mitochondria, and p62 is not required for the recruitment of either optineurin or LC3 to damaged mitochondria. Thus, our study establishes an important role for optineurin as an autophagy receptor in parkin-mediated mitophagy and demonstrates that defects in a single pathway can lead to neurodegenerative diseases with distinct pathologies.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; autophagosome; mitophagy; optineurin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

