Gene network biological validity based on gene-gene interaction relevance
- PMID: 25295303
- PMCID: PMC4175387
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/540679
Gene network biological validity based on gene-gene interaction relevance
Abstract
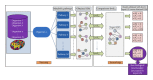
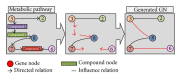
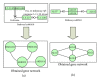
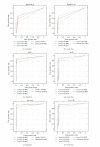
In recent years, gene networks have become one of the most useful tools for modeling biological processes. Many inference gene network algorithms have been developed as techniques for extracting knowledge from gene expression data. Ensuring the reliability of the inferred gene relationships is a crucial task in any study in order to prove that the algorithms used are precise. Usually, this validation process can be carried out using prior biological knowledge. The metabolic pathways stored in KEGG are one of the most widely used knowledgeable sources for analyzing relationships between genes. This paper introduces a new methodology, GeneNetVal, to assess the biological validity of gene networks based on the relevance of the gene-gene interactions stored in KEGG metabolic pathways. Hence, a complete KEGG pathway conversion into a gene association network and a new matching distance based on gene-gene interaction relevance are proposed. The performance of GeneNetVal was established with three different experiments. Firstly, our proposal is tested in a comparative ROC analysis. Secondly, a randomness study is presented to show the behavior of GeneNetVal when the noise is increased in the input network. Finally, the ability of GeneNetVal to detect biological functionality of the network is shown.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prevalent positive epistasis in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic networks.Nat Genet. 2010 Mar;42(3):272-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.524. Epub 2010 Jan 24. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20101242 Free PMC article.
-
A network-based kernel machine test for the identification of risk pathways in genome-wide association studies.Hum Hered. 2013;76(2):64-75. doi: 10.1159/000357567. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Hum Hered. 2013. PMID: 24434848 Free PMC article.
-
Gene network coherence based on prior knowledge using direct and indirect relationships.Comput Biol Chem. 2015 Jun;56:142-51. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2015.03.002. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Comput Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25935118
-
Gene Saturation: An Approach to Assess Exploration Stage of Gene Interaction Networks.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 21;9(1):5017. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41539-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30899072 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Network Inference and analysis using SEBINI and CABIN.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:551-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381531 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive and Systematic Analysis Revealed the Role of ADAR1 in Pan-Cancer Prognosis and Immune Implications.Dis Markers. 2023 Feb 21;2023:7620181. doi: 10.1155/2023/7620181. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 36865502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hecker M, Lambeck S, Toepfer S, van Someren E, Guthke R. Gene regulatory network inference: data integration in dynamic models—a review. BioSystems. 2009;96(1):86–103. - PubMed
-
- Butte AJ, Kohane IS. Mutual information relevance networks: functional genomic clustering using pairwise entropy measurements. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. 2000:418–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

