Central muscarinic cholinergic activation alters interaction between splenic dendritic cell and CD4+CD25- T cells in experimental colitis
- PMID: 25295619
- PMCID: PMC4190311
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109272
Central muscarinic cholinergic activation alters interaction between splenic dendritic cell and CD4+CD25- T cells in experimental colitis
Abstract
Background: The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP) is based on vagus nerve (VN) activity that regulates macrophage and dendritic cell responses in the spleen through alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (a7nAChR) signaling. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients present dysautonomia with decreased vagus nerve activity, dendritic cell and T cell over-activation. The aim of this study was to investigate whether central activation of the CAP alters the function of dendritic cells (DCs) and sequential CD4+/CD25-T cell activation in the context of experimental colitis.
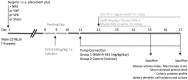
Methods: The dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid model of experimental colitis in C57BL/6 mice was used. Central, intracerebroventricular infusion of the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist McN-A-343 was used to activate CAP and vagus nerve and/or splenic nerve transection were performed. In addition, the role of α7nAChR signaling and the NF-kB pathway was studied. Serum amyloid protein (SAP)-A, colonic tissue cytokines, IL-12p70 and IL-23 in isolated splenic DCs, and cytokines levels in DC-CD4+CD25-T cell co-culture were determined.
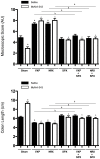
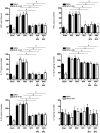
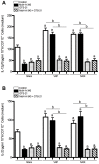
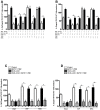
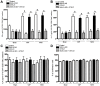
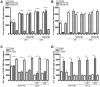
Results: McN-A-343 treatment reduced colonic inflammation associated with decreased pro-inflammatory Th1/Th17 colonic and splenic cytokine secretion. Splenic DCs cytokine release was modulated through α7nAChR and the NF-kB signaling pathways. Cholinergic activation resulted in decreased CD4+CD25-T cell priming. The anti-inflammatory efficacy of central cholinergic activation was abolished in mice with vagotomy or splenic neurectomy.
Conclusions: Suppression of splenic immune cell activation and altered interaction between DCs and T cells are important aspects of the beneficial effect of brain activation of the CAP in experimental colitis. These findings may lead to improved therapeutic strategies in the treatment of IBD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bernstein CN, Papineau N, Zajaczkowski J, Rawsthorne P, Okrusko G, et al. (2000) Direct hospital costs for patients with inflammatory bowel disease in a Canadian tertiary care university hospital. Am J Gastroenterol 95: 677–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

