Deficits in tactile learning in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 25296296
- PMCID: PMC4189789
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109116
Deficits in tactile learning in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome
Abstract
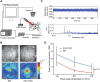
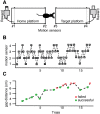
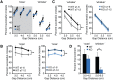
The fragile X mental retardation 1 mutant mouse (Fmr1 KO) recapitulates several of the neurologic deficits associated with Fragile X syndrome (FXS). As tactile hypersensitivity is a hallmark of FXS, we examined the sensory representation of individual whiskers in somatosensory barrel cortex of Fmr1 KO and wild-type (WT) mice and compared their performance in a whisker-dependent learning paradigm, the gap cross assay. Fmr1 KO mice exhibited elevated responses to stimulation of individual whiskers as measured by optical imaging of intrinsic signals. In the gap cross task, initial performance of Fmr1 KO mice was indistinguishable from WT controls. However, while WT mice improved significantly with experience at all gap distances, Fmr1 KO mice displayed significant and specific deficits in improvement at longer distances which rely solely on tactile information from whiskers. Thus, Fmr1 KO mice possess altered cortical responses to sensory input that correlates with a deficit in tactile learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Turner G, Webb T, Wake S, Robinson H (1996) Prevalence of fragile X syndrome. Am J Med Genet 64: 196–197 doi:;10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<196::AID-AJMG35>3.0.CO;2-G - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller LJ, McIntosh DN, McGrath J, Shyu V, Lampe M, et al. (1999) Electrodermal responses to sensory stimuli in individuals with fragile X syndrome: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet 83: 268–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

