Cryopreservation of MHC multimers: Recommendations for quality assurance in detection of antigen specific T cells
- PMID: 25297339
- PMCID: PMC4309491
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.22575
Cryopreservation of MHC multimers: Recommendations for quality assurance in detection of antigen specific T cells
Abstract
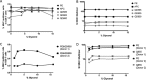
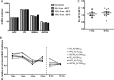
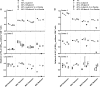
Fluorescence-labeled peptide-MHC class I multimers serve as ideal tools for the detection of antigen-specific T cells by flow cytometry, enabling functional and phenotypical characterization of specific T cells at the single cell level. While this technique offers a number of unique advantages, MHC multimer reagents can be difficult to handle in terms of stability and quality assurance. The stability of a given fluorescence-labeled MHC multimer complex depends on both the stability of the peptide-MHC complex itself and the stability of the fluorochrome. Consequently, stability is difficult to predict and long-term storage is generally not recommended. We investigated here the possibility of cryopreserving MHC multimers, both in-house produced and commercially available, using a wide range of peptide-MHC class I multimers comprising virus and cancer-associated epitopes of different affinities presented by various HLA-class I molecules. Cryopreservation of MHC multimers was feasible for at least 6 months, when they were dissolved in buffer containing 5-16% glycerol (v/v) and 0.5% serum albumin (w/v). The addition of cryoprotectants was tolerated across three different T-cell staining protocols for all fluorescence labels tested (PE, APC, PE-Cy7 and Quantum dots). We propose cryopreservation as an easily implementable method for stable storage of MHC multimers and recommend the use of cryopreservation in long-term immunomonitoring projects, thereby eliminating the variability introduced by different batches and inconsistent stability.
Keywords: MHC multimer; cryopreservation; cryoprotectant; glycerol in T cell staining; quality assurance; recommendations for MHC multimer storage.
© 2014 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Figures



References
-
- Altman JD, Moss PA, Goulder PJ, Barouch DH, McHeyzer-Williams MG, Bell JI, McMichael AJ, Davis MM. Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science. 1996;274:94–96. - PubMed
-
- Appay V, Dunbar PR, Callan M, Klenerman P, Gillespie GM, Papagno L, Ogg GS, King A, Lechner F, Spina CA, et al. Memory CD8+ T cells vary in differentiation phenotype in different persistent virus infections. Nat Med. 2002;8:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Tan LC, Gudgeon N, Annels NE, Hansasuta P, O'Callaghan CA, Rowland-Jones S, McMichael AJ, Rickinson AB, Callan MF. A re-evaluation of the frequency of CD8+ T cells specific for EBV in healthy virus carriers. J Immunol. 1999;162:1827–1835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

