Pin1-dependent signalling negatively affects GABAergic transmission by modulating neuroligin2/gephyrin interaction
- PMID: 25297980
- PMCID: PMC4197815
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6066
Pin1-dependent signalling negatively affects GABAergic transmission by modulating neuroligin2/gephyrin interaction
Abstract
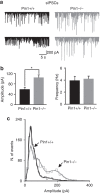
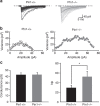
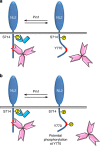
The cell adhesion molecule Neuroligin2 (NL2) is localized selectively at GABAergic synapses, where it interacts with the scaffolding protein gephyrin in the post-synaptic density. However, the role of this interaction for formation and plasticity of GABAergic synapses is unclear. Here, we demonstrate that endogenous NL2 undergoes proline-directed phosphorylation at its unique S714-P consensus site, leading to the recruitment of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase Pin1. This signalling cascade negatively regulates NL2's ability to interact with gephyrin at GABAergic post-synaptic sites. As a consequence, enhanced accumulation of NL2, gephyrin and GABAA receptors was detected at GABAergic synapses in the hippocampus of Pin1-knockout mice (Pin1-/-) associated with an increase in amplitude of spontaneous GABAA-mediated post-synaptic currents. Our results suggest that Pin1-dependent signalling represents a mechanism to modulate GABAergic transmission by regulating NL2/gephyrin interaction.
Figures







References
-
- Levinson J. N. et al. Neuroligins mediate excitatory and inhibitory synapse formation: involvement of PSD-95 and neurexin-1beta in neuroligin-induced synaptic specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 17312–17319 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

