Magneto-fluorescent core-shell supernanoparticles
- PMID: 25298155
- PMCID: PMC4264679
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6093
Magneto-fluorescent core-shell supernanoparticles
Abstract
Magneto-fluorescent particles have been recognized as an emerging class of materials that exhibit great potential in advanced applications. However, synthesizing such magneto-fluorescent nanomaterials that simultaneously exhibit uniform and tunable sizes, high magnetic content loading, maximized fluorophore coverage at the surface and a versatile surface functionality has proven challenging. Here we report a simple approach for co-assembling magnetic nanoparticles with fluorescent quantum dots to form colloidal magneto-fluorescent supernanoparticles. Importantly, these supernanoparticles exhibit a superstructure consisting of a close-packed magnetic nanoparticle 'core', which is fully surrounded by a 'shell' of fluorescent quantum dots. A thin layer of silica coating provides high colloidal stability and biocompatibility, and a versatile surface functionality. We demonstrate that after surface pegylation, these silica-coated magneto-fluorescent supernanoparticles can be magnetically manipulated inside living cells while being optically tracked. Moreover, our silica-coated magneto-fluorescent supernanoparticles can also serve as an in vivo multi-photon and magnetic resonance dual-modal imaging probe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
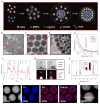
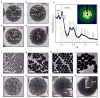

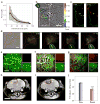
References
-
- Gibson RF. A review of recent research on mechanics of multifunctional composite materials and structures. Compos Struct. 2010;92:2793–2810.
-
- Suh WH, Suh YH, Stucky GD. Multifunctional nanosystems at the interface of physical and life sciences. Nano Today. 2009;4:27–36.
-
- Bigall NC, Parak WJ, Dorfs D. Fluorescent, magnetic and plasmonic-Hybrid multifunctional colloidal nano objects. Nano Today. 2012;7:282–296.
-
- Lee JE, Lee N, Kim T, Kim J, Hyeon T. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocomposite nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Accounts Chem Res. 2011;44:893–902. - PubMed
-
- Macfarlane RJ, et al. Nanoparticle superlattice engineering with DNA. Science. 2011;334:204–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS076462/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA028299/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-NS076462/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA080124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA096915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-U54-CA151884/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA163815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151884/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 9-P41-EB015871-26A1/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA028299/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA080124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA126642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA096915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015871/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

