c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-κB-dependent TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 25299780
- PMCID: PMC4237244
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.417
c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-κB-dependent TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
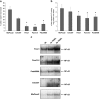
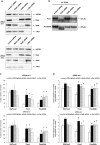
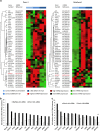
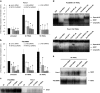
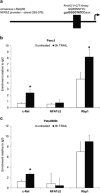
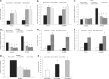
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) represents one of the deadliest malignancies with an overall life expectancy of 6 months despite current therapies. NF-κB signalling has been shown to be critical for this profound cell-autonomous resistance against chemotherapeutic drugs and death receptor-induced apoptosis, but little is known about the role of the c-Rel subunit in solid cancer and PDAC apoptosis control. In the present study, by analysis of genome-wide patterns of c-Rel-dependent gene expression, we were able to establish c-Rel as a critical regulator of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in PDAC. TRAIL-resistant cells exhibited a strong TRAIL-inducible NF-κB activity, whereas TRAIL-sensitive cells displayed only a small increase in NF-κB-binding activity. Transfection with siRNA against c-Rel sensitized the TRAIL-resistant cells in a manner comparable to siRNA targeting the p65/RelA subunit. Gel-shift analysis revealed that c-Rel is part of the TRAIL-inducible NF-κB complex in PDAC. Array analysis identified NFATc2 as a c-Rel target gene among the 12 strongest TRAIL-inducible genes in apoptosis-resistant cells. In line, siRNA targeting c-Rel strongly reduced TRAIL-induced NFATc2 activity in TRAIL-resistant PDAC cells. Furthermore, siRNA targeting NFATc2 sensitized these PDAC cells against TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Finally, TRAIL-induced expression of COX-2 was diminished through siRNA targeting c-Rel or NFATc2 and pharmacologic inhibition of COX-2 with celecoxib or siRNA targeting COX-2, enhanced TRAIL apoptosis. In conclusion, we were able to delineate a novel c-Rel-, NFATc2- and COX-2-dependent antiapoptotic signalling pathway in PDAC with broad clinical implications for pharmaceutical intervention strategies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of CCL20 mediated immune cell recruitment in NF-κB mediated TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 May;1864(5):782-796. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28188806
-
NF-κB/RelA controlled A20 limits TRAIL-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jan 3;14(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05535-9. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36596765 Free PMC article.
-
Differential roles of RelA (p65) and c-Rel subunits of nuclear factor kappa B in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand signaling.Cancer Res. 2003 Mar 1;63(5):1059-66. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12615723
-
Advancement of NF-κB Signaling Pathway: A Novel Target in Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3890. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123890. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB/Rel transcriptional pathway: implications in pancreatic cancer.Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2002;31(1-3):71-8. doi: 10.1385/IJGC:31:1-3:71. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12622417 Review.
Cited by
-
ROCK2 mediates osteosarcoma progression and TRAIL resistance by modulating O-GlcNAc transferase degradation.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 1;10(3):781-798. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32266091 Free PMC article.
-
High-depth, high-accuracy microsatellite genotyping enables precision lung cancer risk classification.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 16;36(46):6383-6390. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.256. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28759038 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of two functional variants in the human longevity gene FOXO3.Nat Commun. 2017 Dec 12;8(1):2063. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02183-y. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29234056 Free PMC article.
-
ELF3 plays an important role in defining TRAIL sensitivity in breast cancer by modulating the expression of decoy receptor 2 (DCR2).Mol Biol Rep. 2024 May 24;51(1):671. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09615-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38787503
-
Constitutive activation and overexpression of NF-κB/c-Rel in conjunction with p50 contribute to aggressive tongue tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 31;9(68):33011-33029. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26041. eCollection 2018 Aug 31. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30250646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30. - PubMed
-
- 2Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 1817–1825. - PubMed
-
- 4Arlt A, Muerkoster SS, Schafer H. Targeting apoptosis pathways in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 2013; 332: 346–358. - PubMed
-
- 5Wormann SM, Diakopoulos KN, Lesina M, Algul H. The immune network in pancreatic cancer development and progression. Oncogene 2013; 33: 2956–2967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

