National trends in hospitalization and mortality rates for patients with HIV, HCV, or HIV/HCV coinfection from 1996-2010 in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 25300638
- PMCID: PMC4287456
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-536
National trends in hospitalization and mortality rates for patients with HIV, HCV, or HIV/HCV coinfection from 1996-2010 in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The comparative impact of chronic viral monoinfection versus coinfection on inpatient outcomes and health care utilization is relatively unknown. This study examined trends, inpatient utilization, and hospital outcomes for patients with HIV, HCV, or HIV/HCV coinfection.
Methods: Data were from the 1996-2010 National Hospital Discharge Surveys. Hospitalizations with primary ICD-9-CM codes for HIV or HCV were included for HIV and HCV monoinfection, respectfully. Coinfection included both HIV and HCV codes. Demographic characteristics, select comorbidities, procedural interventions, average hospital length of stay (LOS), and discharge status were compared by infection status (HIV, HCV, HIV/HCV). Annual disease estimates and survey weights were used to generate hospitalization rates.
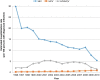
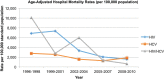
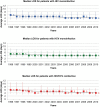
Results: ~6.6 million hospitalizations occurred in patients with HIV (39%), HCV (56%), or HIV/HCV (5%). The hospitalization rate (hospitalizations per 100 persons with infection) decreased in the HIV group (29.8 in 1996; 5.3 in 2010), decreased in the HIV/HCV group (2.0 in 1996; 1.5 in 2010), yet increased in the HCV group (0.2 in 1996; 0.9 in 2010). Median LOS from 1996 to 2010 (days, interquartile range) decreased in all groups: HIV, 6 (3-10) to 4 (3-8); HCV, 5 (3-9) to 4 (2-6); HIV/HCV, 6 (4-11) to 4 (2-7). Age-adjusted mortality rates decreased for all three groups. The rate of decline was least pronounced for those with HCV monoinfection.
Conclusion: Hospitalizations have declined more rapidly for patients with HIV infection (including HIV/HCV coinfection) than for patients with HCV infection. This growing disparity between HIV and HCV underscores the need to allocate more resources to HCV care in hopes that similar large-scale improvements can also be accomplished for patients with HCV.
Figures
References
-
- Linas BP, Wang B, Smurzynski M, Losina E, Bosch RJ, Schackman BR, Rong J, Sax PE, Walensky RP, Schouten J, Freedberg KA. The impact of HIV/HCV co-infection on health care utilization and disability: results of the ACTG Longitudinal Linked Randomized Trials (ALLRT) Cohort. J Viral Hepat. 2011;18(7):506–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2010.01325.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Katzenstein DA, Hammer SM, Hughes MD, Gundacker H, Jackson JB, Fiscus S, Rasheed S, Elbeik T, Reichman R, Japour A, Merigan TC, Hirsch MS. The relation of virologic and immunologic markers to clinical outcomes after nucleoside therapy in HIV-infected adults with 200 to 500 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter. AIDS Clinical Trials Group Study 175 Virology Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(15):1091–1098. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199610103351502. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Schiff ER, Shiffman ML, Lee WM, Rustgi VK, Goodman ZD, Ling MH, Cort S, Albrecht JK. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(21):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811193392101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Torriani FJ, Rodriguez-Torres M, Rockstroh JK, Lissen E, Gonzalez-Garcia J, Lazzarin A, Carosi G, Sasadeusz J, Katlama C, Montaner J, Sette H, Jr, Passe S, De Pamphilis J, Duff F, Schrenk UM, Dieterich DT. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection in HIV-infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(5):438–450. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040842. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2334/14/536/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

