Managing high-risk CLL during transition to a new treatment era: stem cell transplantation or novel agents?
- PMID: 25301705
- PMCID: PMC4276025
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-586826
Managing high-risk CLL during transition to a new treatment era: stem cell transplantation or novel agents?
Abstract
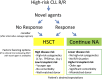
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been considered as the treatment of choice for patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (HR-CLL; ie, refractory to purine analogs, short response [<24 months] to chemoimmunotherapy, and/or presence of del[17p]/TP53 mutations). Currently, treatment algorithms for HR-CLL are being challenged by the introduction of novel classes of drugs. Among them, BCR signal inhibitors (BCRi) and B-cell lymphoma 2 antagonists (BCL2a) appear particularly promising. As a result of the growing body of favorable outcome data reported for BCRi/BCL2a, uncertainty is emerging on how to advise patients with HR-CLL about indication for and timing of HSCT. This article provides an overview of currently available evidence and theoretical considerations to guide this difficult decision process. Until the risks and benefits of different treatment strategies are settled, all patients with HR-CLL should be considered for treatment with BCRi/BCL2a. For patients who respond to these agents, there are 2 treatment possibilities: (1) performing an HSCT or (2) continuing treatment with the novel drug. Individual disease-specific and transplant-related risk factors, along with patient's preferences, should be taken into account when recommending one of these treatments over the other.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Transplant for CLL: still an option?Blood. 2014 Dec 18;124(26):3835-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-606871. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25525078 No abstract available.
References
-
- Keating MJ, O’Brien S, Albitar M, et al. Early results of a chemoimmunotherapy regimen of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as initial therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(18):4079–4088. - PubMed
-
- Byrd JC, Gribben JG, Peterson BL, et al. Select high-risk genetic features predict earlier progression following chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine and rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: justification for risk-adapted therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(3):437–443. - PubMed
-
- Bosch F, Abrisqueta P, Villamor N, et al. Rituximab, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and mitoxantrone: a new, highly active chemoimmunotherapy regimen for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(27):4578–4584. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. International Group of Investigators; German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Study Group. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164–1174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous