Androgen receptor promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via AKT-phosphorylation dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9
- PMID: 25301736
- PMCID: PMC4279395
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2513
Androgen receptor promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via AKT-phosphorylation dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Androgen receptor promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via AKT-phosphorylation dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9.Oncotarget. 2025 May 29;16:410. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28736. Oncotarget. 2025. PMID: 40439455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
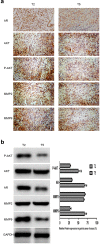
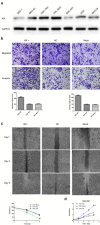
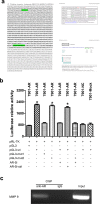
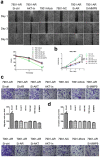
Androgen receptor (AR) plays an important role in many kinds of cancers. However, the molecular mechanisms of AR in gastric cancer (GC) are poorly characterized. Here, we investigated the role of AR in GC cell migration, invasion and metastatic potential. Our data showed that AR expression was positively correlated with lymph node metastasis and late TNM stages. These findings were accompanied by activation of AKT and upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9). AR overexpression induced increases in GC cell migration, invasion and proliferation in vitro and in vivo. These effects were attenuated by inhibition of AKT, AR and MMP9. AR overexpression upregulated MMP9 protein levels, whereas this effect was counteracted by AR siRNA. Inhibition of AKT by siRNA or an inhibitor (MK-2206 2HC) decreased AR protein expression in both stably transfected and parental SGC-7901 cells. Luciferase reporter and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that AR bound to the AR-binding sites of the MMP9 promoter. In summary, AR overexpression induced by AKT phosphorylation upregulated MMP9 by binding to its promoter region to promote gastric carcinogenesis. The AKT/AR/MMP9 pathway plays an important role in GC metastasis and may be a novel therapeutic target for GC treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
There no potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Negi SS, Agarwal A, Chaudhary A. Flutamide in unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Invest New Drugs. 2006;24(3):189–194. - PubMed
-
- Chen PJ, Yeh SH, Liu WH, Lin CC, Huang HC, Chen CL, Chen DS, Chen PJ. Androgen pathway stimulates MicroRNA-216a transcription to suppress the tumor suppressor in lung cancer-1 gene in early hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2012;56(2):632–643. - PubMed
-
- Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD, Gatta G, de Braud F, Van Cutsem E. Gastric cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2009;71(2):127–164. - PubMed
-
- Feng H, Cheng ASL, Tsang DP, Li MS, Go MY, Cheung YS, Zhao GJ, Ng SS, Lin MC, Yu J, Lai PB, To KF, Sung JJY. Cell cycle-related kinase is a direct androgen receptor-regulated gene that drives beta-catenin/T cell factor-dependent hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(8):3159–3175. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

