Optimal management of elderly cancer patients: usefulness of the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
- PMID: 25302022
- PMCID: PMC4189720
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S57849
Optimal management of elderly cancer patients: usefulness of the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
Abstract
Background: Cancer is common in older patients, who raise specific treatment challenges due to aging-related, organ-specific physiologic changes and the presence in most cases of comorbidities capable of affecting treatment tolerance and outcomes. Identifying comorbid conditions and physiologic changes due to aging allows oncologists to better assess the risk/benefit ratio and to adjust the treatment accordingly. Conducting a Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) is one approach developed for this purpose. We reviewed the evidence on the usefulness of CGA for assessing health problems and predicting cancer treatment outcomes, functional decline, morbidity, and mortality in older patients with solid malignancies.
Methods: We searched Medline for articles published in English between January 1, 2000 and April 14, 2014, and reporting prospective observational or interventional studies of CGA feasibility or effectiveness in patients aged ≥65 years with solid malignancies. We identified studies with at least 100 patients, a multivariate analysis, and assessments of at least five of the following CGA domains: nutrition, cognition, mood, functional status, mobility and falls, polypharmacy, comorbidities, and social environment.
Results: All types of CGA identified a large number of unrecognized health problems capable of interfering with cancer treatment. CGA results influenced 21%-49% of treatment decisions. All CGA domains were associated with chemotoxicity or survival in at least one study. The abnormalities that most often predicted mortality and chemotoxicity were functional impairment, malnutrition, and comorbidities.
Conclusion: The CGA uncovers numerous health problems in elderly patients with cancer and can affect treatment decisions. Functional impairment, malnutrition, and comorbidities are independently associated with chemotoxicity and/or survival. Only three randomized published studies evaluated the effectiveness of CGA-linked interventions. Further research into the effectiveness of the CGA in improving patient outcomes is needed.
Keywords: cancer; chemotoxicity; elderly; geriatric assessment; mortality; outcomes.
Figures
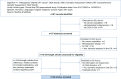
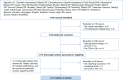
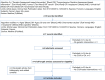
References
-
- Smith BD, Smith GL, Hurria A, Hortobagyi GN, Buchholz TA. Future of cancer incidence in the United States: burdens upon an aging, changing nation. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(17):2758–2765. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Karim-Kos HE, Coebergh JW, et al. Recent trends in incidence of five common cancers in 26 European countries since 1988: analysis of the European Cancer Observatory. Eur J Cancer. 2013 Oct 8; [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Scher KS, Hurria A. Under-representation of older adults in cancer registration trials: known problem, little progress. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(17):2036–2038. - PubMed
-
- Turrentine FE, Wang H, Simpson VB, Jones RS. Surgical risk factors, morbidity, and mortality in elderly patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;203(6):865–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

