Functional optoacoustic human angiography with handheld video rate three dimensional scanner
- PMID: 25302151
- PMCID: PMC4134902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2013.10.002
Functional optoacoustic human angiography with handheld video rate three dimensional scanner
Abstract
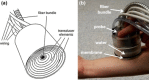
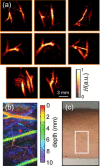
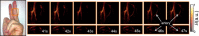
Optoacoustic imaging provides a unique combination of high optical contrast and excellent spatial resolution, making it ideal for simultaneous imaging of tissue anatomy as well as functional and molecular contrast in deep optically opaque tissues. We report on development of a portable clinical system for three-dimensional optoacoustic visualization of deep human tissues at video rate. Studies in human volunteers have demonstrated powerful performance in delivering high resolution volumetric multispectral optoacoustic tomography (vMSOT) images of tissue morphology and function, such as blood oxygenation parameters, in real time. Whilst most imaging modalities currently in clinical use are not able to deliver volumetric data with comparable time resolution, the presented imaging approach holds promise to attain new diagnostic and treatment monitoring value for multiple indications, such as cardiovascular and peripheral vascular disease, disorders related to the lymphatic system, breast lesions, arthritis and inflammation.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diagnostics; Functional and molecular imaging; Optoacoustic imaging.
Figures

References
-
- McGahan J.P., Goldberg B.B. Informa UK Ltd.; 2008. Diagnostic ultrasound.
-
- Devuyst G. Ultrasound measurement of the fibrous cap in symptomatic and asymptomatic atheromatous carotid plaques. Circulation. 2005;111:2776–2782. - PubMed
-
- Kelley L.L., Petersen C.M. Mosby; St. Louis, MO: 2012. Sectional anatomy for imaging professionals.
-
- Von Schulthess G.K. Lippincott Williams & Wilkin; Philadelphia, PA: 2007. Molecular anatomic imaging: pet-CT and spect-CT integrated modality imaging.
-
- Lee J.H. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nature Medicine. 2007;13:95–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

