Identification of causal genetic drivers of human disease through systems-level analysis of regulatory networks
- PMID: 25303533
- PMCID: PMC4194029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.021
Identification of causal genetic drivers of human disease through systems-level analysis of regulatory networks
Erratum in
-
Identification of Causal Genetic Drivers of Human Disease through Systems-Level Analysis of Regulatory Networks.Cell. 2016 Aug 11;166(4):1055. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.036. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27518566 No abstract available.
Abstract
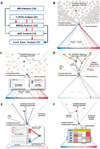
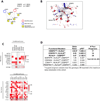
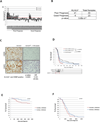
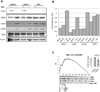
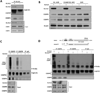
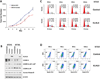
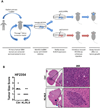
Identification of driver mutations in human diseases is often limited by cohort size and availability of appropriate statistical models. We propose a framework for the systematic discovery of genetic alterations that are causal determinants of disease, by prioritizing genes upstream of functional disease drivers, within regulatory networks inferred de novo from experimental data. We tested this framework by identifying the genetic determinants of the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma. Our analysis uncovered KLHL9 deletions as upstream activators of two previously established master regulators of the subtype, C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ. Rescue of KLHL9 expression induced proteasomal degradation of C/EBP proteins, abrogated the mesenchymal signature, and reduced tumor viability in vitro and in vivo. Deletions of KLHL9 were confirmed in > 50% of mesenchymal cases in an independent cohort, thus representing the most frequent genetic determinant of the subtype. The method generalized to study other human diseases, including breast cancer and Alzheimer's disease.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Lefebvre C, Alvarez MJ, Castillo-Martin M, Zheng T, Eastham JA, Gopalan A, Pienta K, Shen MM, et al. Cross-species analysis of genome-wide regulatory networks identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1 and CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy. Cancer Cell. 2014a;25:638–651. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Lefebvre C, Alvarez MJ, Castillo-Martin M, Zheng T, Eastham JA, Gopalan A, Pienta KJ, Shen MM, et al. Cross-species regulatory network analysis identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1 and CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy. Cancer Cell. 2014b;25:638–651. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basso K, Margolin AA, Stolovitzky G, Klein U, Dalla-Favera R, Califano A. Reverse engineering of regulatory networks in human B cells. Nat Genet. 2005;37:382–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM082797/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148308/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA121852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA168426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2CA148308-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007088/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS061776-05/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA168397/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA121852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA154293/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS061776/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM082797/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01CA16842603/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA154293/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA127001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

