Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens
- PMID: 25305756
- PMCID: PMC4213311
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3118
Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens
Abstract
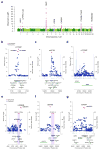
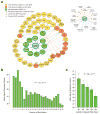
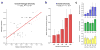
We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of IgA nephropathy (IgAN), the most common form of glomerulonephritis, with discovery and follow-up in 20,612 individuals of European and East Asian ancestry. We identified six new genome-wide significant associations, four in ITGAM-ITGAX, VAV3 and CARD9 and two new independent signals at HLA-DQB1 and DEFA. We replicated the nine previously reported signals, including known SNPs in the HLA-DQB1 and DEFA loci. The cumulative burden of risk alleles is strongly associated with age at disease onset. Most loci are either directly associated with risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or maintenance of the intestinal epithelial barrier and response to mucosal pathogens. The geospatial distribution of risk alleles is highly suggestive of multi-locus adaptation, and genetic risk correlates strongly with variation in local pathogens, particularly helminth diversity, suggesting a possible role for host-intestinal pathogen interactions in shaping the genetic landscape of IgAN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R03DK099564/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079310/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK090207/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK098531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK099564/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21DK09853/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G1002528/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK090207/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095510/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK095510/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

