Ormeloxifene efficiently inhibits ovarian cancer growth
- PMID: 25306892
- PMCID: PMC4391643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.009
Ormeloxifene efficiently inhibits ovarian cancer growth
Abstract
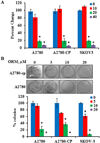
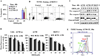
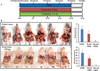
Ovarian cancer continues to be a leading cause of cancer related deaths for women. Anticancer agents effective against chemo-resistant cells are greatly needed for ovarian cancer treatment. Repurposing drugs currently in human use is an attractive strategy for developing novel cancer treatments with expedited translation into clinical trials. Therefore, we examined whether ormeloxifene (ORM), a non-steroidal Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (SERM) currently used for contraception, is therapeutically effective at inhibiting ovarian cancer growth. We report that ORM treatment inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cell lines, including cell lines resistant to cisplatin. Furthermore, ORM treatment decreases Akt phosphorylation, increases p53 phosphorylation, and modulates the expression and localization patterns of p27, cyclin E, cyclin D1, and CDK2. In a pre-clinical xenograft mouse ORM treatment significantly reduces tumorigenesis and metastasis. These results indicate that ORM effectively inhibits the growth of cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells. ORM is currently in human use and has an established record of patient safety. Our encouraging in vitro and pre-clinical in vivo findings indicate that ORM is a promising candidate for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cisplatin resistance; Novel therapies; Ormeloxifene; Ovarian cancer; Xenograft mice.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no financial and non-financial competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Bansode FW, Chauhan SC, Makker A, Singh MM. Uterine luminal epithelial alkaline phosphatase activity and pinopod development in relation to endometrial sensitivity in the rat. Contraception. 1998;58:61–68. - PubMed
-
- Kamboj VP, Setty BS, Chandra H, Roy SK, Kar AB. Biological profile of Centchroman--a new post-coital contraceptive. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1977;15:1144–1150. - PubMed
-
- Misra NC, Nigam PK, Gupta R, Agarwal AK, Kamboj VP. Centchroman--a non-steroidal anti-cancer agent for advanced breast cancer: phase-II study. Int. J. Cancer. 1989;43:781–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

