Human intracellular ISG15 prevents interferon-α/β over-amplification and auto-inflammation
- PMID: 25307056
- PMCID: PMC4303590
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13801
Human intracellular ISG15 prevents interferon-α/β over-amplification and auto-inflammation
Abstract
Intracellular ISG15 is an interferon (IFN)-α/β-inducible ubiquitin-like modifier which can covalently bind other proteins in a process called ISGylation; it is an effector of IFN-α/β-dependent antiviral immunity in mice. We previously published a study describing humans with inherited ISG15 deficiency but without unusually severe viral diseases. We showed that these patients were prone to mycobacterial disease and that human ISG15 was non-redundant as an extracellular IFN-γ-inducing molecule. We show here that ISG15-deficient patients also display unanticipated cellular, immunological and clinical signs of enhanced IFN-α/β immunity, reminiscent of the Mendelian autoinflammatory interferonopathies Aicardi-Goutières syndrome and spondyloenchondrodysplasia. We further show that an absence of intracellular ISG15 in the patients' cells prevents the accumulation of USP18, a potent negative regulator of IFN-α/β signalling, resulting in the enhancement and amplification of IFN-α/β responses. Human ISG15, therefore, is not only redundant for antiviral immunity, but is a key negative regulator of IFN-α/β immunity. In humans, intracellular ISG15 is IFN-α/β-inducible not to serve as a substrate for ISGylation-dependent antiviral immunity, but to ensure USP18-dependent regulation of IFN-α/β and prevention of IFN-α/β-dependent autoinflammation.
Figures
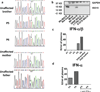







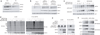
Comment in
-
Cytokines: ISG15--human deficiency reveals new proficiency.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Dec;14(12):780-1. doi: 10.1038/nri3767. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25359440 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- BioProject/PRJNA167660
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P01AI090935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI035237/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AI106942/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI083025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI095983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 8UL1TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI083025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI076210/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00AI106942-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI090935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01AI076210-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 309449/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- R37AI095983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

