Climate, demographic factors and geographical variations in the incidence of invasive meningococcal disease in Italy
- PMID: 25308801
- PMCID: PMC9507234
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268814002659
Climate, demographic factors and geographical variations in the incidence of invasive meningococcal disease in Italy
Abstract
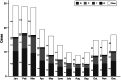
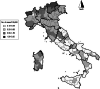
We investigated the effect of climatic, demographic factors and intra-country geographical variations on the incidence of invasive meningococcal disease (IMD) in Italy. For this purpose, incidence rates of IMD cases reported in Italy between 1994 and 2012 were calculated, and a cluster analysis was performed. A geographical gradient was determined, with lower incidence rates in central and southern Italy, compared to the northern parts, where most clusters were observed. IMD rates were higher in medium-sized towns than in villages. Adults were at lower risk of IMD than children aged ⩽4 years. IMD incidence tended to decrease with increasing monthly mean temperatures (incidence rate ratio 0·94, 95% confidence interval 0·90-0·99). In conclusion, geographical variations in IMD incidence were found, where age and temperature were associated with disease occurrence. Whether geographical variations should be considered in national intervention plans is still a matter for discussion.
Keywords: IMD incidence.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Trotter CL, Greenwood BM. Meningococcal carriage in the African meningitis belt. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2007; 7: 797–803. - PubMed
-
- ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report 2013. (http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/annual-epidemiolo...). 2014.
-
- Stuart JM, et al. Effect of smoking on meningococcal carriage. Lancet 1989. September 23; 2: 723–5. - PubMed
-
- Magoni M, et al. Do environmental factors influence the occurrence of acute meningitis in industrialized countries? An epidemic of varying aetiology in Northern Italy. European Journal of Epidemiology 2006; 21: 465–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

