Studentized continuous wavelet transform (t-CWT) in the analysis of individual ERPs: real and simulated EEG data
- PMID: 25309308
- PMCID: PMC4160090
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00279
Studentized continuous wavelet transform (t-CWT) in the analysis of individual ERPs: real and simulated EEG data
Abstract
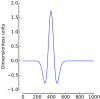
This study aimed at evaluating the performance of the Studentized Continuous Wavelet Transform (t-CWT) as a method for the extraction and assessment of event-related brain potentials (ERP) in data from a single subject. Sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive values (NPV) of the t-CWT were assessed and compared to a variety of competing procedures using simulated EEG data at six low signal-to-noise ratios. Results show that the t-CWT combines high sensitivity and specificity with favorable PPV and NPV. Applying the t-CWT to authentic EEG data obtained from 14 healthy participants confirmed its high sensitivity. The t-CWT may thus be well suited for the assessment of weak ERPs in single-subject settings.
Keywords: EEG; ERP; detection; electroencephalogram; significance; t-CWT; wavelet.
Figures




References
-
- Abramovich F., Benjamini Y. (1995). Thresholding of wavelet coefficients as multiple hypotheses testing procedure, in Lecture Notes in Statistics, eds Bickel P., Diggle P., Fienberg S., Krickeberg K., Olkin I., Wermuth N. (New York, NY: Springer New York; ), 5–14
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 57, 289–300
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

