Uncertainties associated with assessing the public health risk from Legionella
- PMID: 25309526
- PMCID: PMC4174118
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00501
Uncertainties associated with assessing the public health risk from Legionella
Abstract
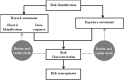
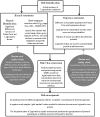
Legionella is an opportunistic pathogen of public health concern. Current regulatory and management guidelines for the control of this organism are informed by risk assessments. However, there are many unanswered questions and uncertainties regarding Legionella epidemiology, strain infectivity, infectious dose, and detection methods. This review follows the EnHealth Risk Assessment Framework, to examine the current information available regarding Legionella risk and discuss the uncertainties and assumptions. This review can be used as a tool for understanding the uncertainties associated with Legionella risk assessment. It also serves to highlight the areas of Legionella research that require future focus. Improvement of these uncertainties will provide information to enhance risk management practices for Legionella, potentially improving public health protection and reducing the economic costs by streamlining current management practices.
Keywords: L. pneumophila; Legionella; Legionellosis; QMRA; public health; risk assessment.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed W., Vieritz A., Goonetilleke A., Gardner T. (2010). Health risk from the use of roof-harvested rainwater in Southeast Queensland, Australia, as potable or nonpotable water, determined using quantitative microbial risk assessment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76 7382–7391 10.1128/aem.00944-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allegra S., Grattard F., Girardot F., Riffard S., Pozzetto B., Berthelot P. (2011). Longitudinal evaluation of the efficacy of heat treatment procedures against Legionella spp. in hospital water systems by using a flow cytometric assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77 1268–1275 10.1128/AEM.02225-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources