The Dalton quantum chemistry program system
- PMID: 25309629
- PMCID: PMC4171759
- DOI: 10.1002/wcms.1172
The Dalton quantum chemistry program system
Abstract
Dalton is a powerful general-purpose program system for the study of molecular electronic structure at the Hartree-Fock, Kohn-Sham, multiconfigurational self-consistent-field, Møller-Plesset, configuration-interaction, and coupled-cluster levels of theory. Apart from the total energy, a wide variety of molecular properties may be calculated using these electronic-structure models. Molecular gradients and Hessians are available for geometry optimizations, molecular dynamics, and vibrational studies, whereas magnetic resonance and optical activity can be studied in a gauge-origin-invariant manner. Frequency-dependent molecular properties can be calculated using linear, quadratic, and cubic response theory. A large number of singlet and triplet perturbation operators are available for the study of one-, two-, and three-photon processes. Environmental effects may be included using various dielectric-medium and quantum-mechanics/molecular-mechanics models. Large molecules may be studied using linear-scaling and massively parallel algorithms. Dalton is distributed at no cost from http://www.daltonprogram.org for a number of UNIX platforms.
Figures

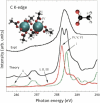
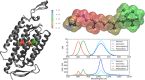
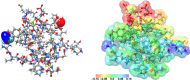
References
-
- Jensen HJAa, Ågren H. Documentation of SIRIUS: A General Purpose Direct Second Order MCSCF Program. Technical Notes TN783, TN784, TN785. Department of Quantum Chemistry, University of Uppsala, Uppsala, Sweden; 1986.
-
- Teale AM, De Proft F, Tozer DJ. Orbital energies and negative electron affinities from density functional theory: insight from the integer discontinuity. J Chem Phys. 2008;129:044110. - PubMed
-
- Rinkevicius Z, Tunell I, Salek P, Vahtras O, Ågren H. Restricted density functional theory of linear time-dependent properties in open-shell molecules. J Chem Phys. 2003;119:34–46.
-
- Oprea O, Telyatnyk L, Rinkevicius Z, Vahtras O, Ågren H. Time-dependent density functional theory with the generalized restricted-unrestricted approach. J Chem Phys. 2006;124:174103. - PubMed
-
- Jensen HJAa, Ågren H. MCSCF optimization using the direct, restricted step, second order norm-extended optimization method. Chem Phys Lett. 1984;110:140–144.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
