Serial changes of neointimal tissue after everolimus-eluting stent implantation in porcine coronary artery: an optical coherence tomography analysis
- PMID: 25309929
- PMCID: PMC4182891
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/851676
Serial changes of neointimal tissue after everolimus-eluting stent implantation in porcine coronary artery: an optical coherence tomography analysis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Serial Changes of Neointimal Tissue after Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation in Porcine Coronary Artery: An Optical Coherence Tomography Analysis".Biomed Res Int. 2019 Nov 21;2019:8629375. doi: 10.1155/2019/8629375. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31871944 Free PMC article.
Abstract
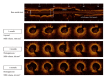
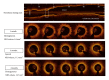
Purposes: The serial changes in neointimal tissues were compared between everolimus-eluting stent (EES) and bare-metal stent (BMS) in the porcine coronary artery using optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Methods: Serial (1, 3, and 6 month follow-up after stent implantation) OCT examinations were performed in 15 swine with 15 BMS- and 15 EES-treated lesions in porcine coronary arteries.
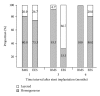
Results: In BMS-implanted lesions, neointimal volume decreased from 7.3 mm(3) to 6.9 mm(3) and 6.4 mm(3) at 1, 3, and 6 months follow-up without statistical significance (P = 0.369). At the time points of 1, 3, and 6 months, neointimal tissue appearance was mainly a homogeneous pattern (80.0%, 93.3%, and 100%, resp.), while the other pattern was layered. In contrast, in EES-implanted lesions, neointimal volume significantly increased from 4.8 mm(3) to 9.8 mm(3) between 1 and 3 months but significantly decreased to 8.6 mm(3) between 3 and 6 months (P < 0.001). Between 1 and 3 months, the layered pattern of neointimal tissue increased from 26.7% to 66.7% but decreased to 20.0% between 3 and 6 months.
Conclusions: EES had a biphasic pattern of neointimal amounts that correlated with changes in neointimal morphology.
Figures



References
-
- Kirtane AJ, Gupta A, Iyengar S, et al. Safety and efficacy of drug-eluting and bare metal stents: comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized trials and observational studies. Circulation. 2009;119(25):3198–3206. - PubMed
-
- Liistro F, Fineschi M, Angioli P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of sirolimus stent implantation for coronary in-stent restenosis. The true (tuscany registry of sirolimus for unselected in-stent restenosis) registry. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2006;48(2):270–275. - PubMed
-
- Murata A, Wallace-Bradley D, Tellez A, et al. Accuracy of optical coherence tomography in the evaluation of neointimal coverage after stent implantation. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2010;3(1):76–84. - PubMed
-
- Prati F, Regar E, Mintz GS, et al. Expert review document on methodology, terminology, and clinical applications of optical coherence tomography: Physical principles, methodology of image acquisition, and clinical application for assessment of coronary arteries and atherosclerosis. European Heart Journal. 2010;31(4):401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

