Characterization of PHB1 and its role in mitochondrial maturation and yolk platelet degradation during development of Artemia embryos
- PMID: 25310573
- PMCID: PMC4195616
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109152
Characterization of PHB1 and its role in mitochondrial maturation and yolk platelet degradation during development of Artemia embryos
Abstract
Background: To cope with harsh environments, crustaceans such as Artemia produce diapause gastrula embryos (cysts) with suppressed metabolism. Metabolism and development resume during post-diapause development, but the mechanism behind these cellular events remains largely unknown.
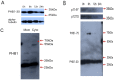
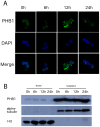
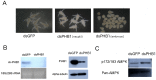
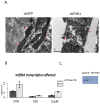
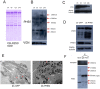
Principal finding: Our study investigated the role of prohibitin 1 (PHB1) in metabolic reinitiation during post-diapause development. We found that PHB1 was developmentally regulated via changes in phosphorylation status and localization. Results from RNA interference experiments demonstrated PHB1 to be critical for mitochondrial maturation and yolk degradation during development. In addition, PHB1 was present in yolk platelets, and it underwent ubiquitin-mediated degradation during the proteolysis of yolk protein.
Conclusions/significance: PHB1 has an indispensable role in coordinating mitochondrial maturation and yolk platelet degradation during development in Artemia. This novel function of PHB1 provides new clues to comprehend the roles of PHB1 in metabolism and development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mishra S, Murphy LC, Nyomba BLG, Murphy LJ (2005) Prohibitin: a potential target for new therapeutics. Trends in Molecular Medicine 11: 192–197. - PubMed
-
- Faller DV, Zhang BH, Sheng W (2002) Prohibitin recruits the chromatin-remodeling ATPases Brg-1 and Brm for repression of E2F-driven transcription and cell proliferation. Blood 100: 738A–738A.
-
- Fusaro G, Wang S, Chellappan S (2002) Differential regulation of Rb family proteins and prohibitin during camptothecin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 21: 4539–4548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

