Combination of TRAIL with bortezomib shifted apoptotic signaling from DR4 to DR5 death receptor by selective internalization and degradation of DR4
- PMID: 25310712
- PMCID: PMC4195680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109756
Combination of TRAIL with bortezomib shifted apoptotic signaling from DR4 to DR5 death receptor by selective internalization and degradation of DR4
Abstract
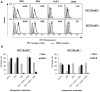
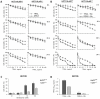
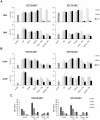
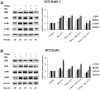
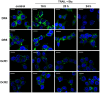
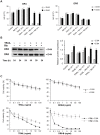
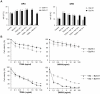
TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) mediates apoptosis in cancer cells through death receptors DR4 and DR5 preferring often one receptor over another in the cells expressing both receptors. Receptor selective mutant variants of TRAIL and agonistic antibodies against DR4 and DR5 are highly promising anticancer agents. Here using DR5 specific mutant variant of TRAIL--DR5-B we have demonstrated for the first time that the sensitivity of cancer cells can be shifted from one TRAIL death receptor to another during co-treatment with anticancer drugs. First we have studied the contribution of DR4 and DR5 in HCT116 p53+/+ and HCT116 p53-/- cells and demonstrated that in HCT116 p53+/+ cells the both death receptors are involved in TRAIL-induced cell death while in HCT116 p53-/- cells prevailed DR4 signaling. The expression of death (DR4 and DR5) as well as decoy (DcR1 and DcR2) receptors was upregulated in the both cell lines either by TRAIL or by bortezomib. However, combined treatment of cells with two drugs induced strong time-dependent and p53-independent internalization and further lysosomal degradation of DR4 receptor. Interestingly DR5-B variant of TRAIL which do not bind with DR4 receptor also induced elimination of DR4 from cell surface in combination with bortezomib indicating the ligand-independent mechanism of the receptor internalization. Eliminatory internalization of DR4 resulted in activation of DR5 receptor thus DR4-dependent HCT116 p53-/- cells became highly sensitive to DR5-B in time-dependent manner. Internalization and degradation of DR4 receptor depended on activation of caspases as well as of lysosomal activity as it was completely inhibited by Z-VAD-FMK, E-64 and Baf-A1. In light of our findings, it is important to explore carefully which of the death receptors is active, when sensitizing drugs are combined with agonistic antibodies to the death receptors or receptor selective variants of TRAIL to enhance cancer treatment efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
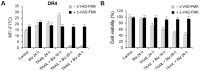
Similar articles
-
Bortezomib sensitizes malignant human glioma cells to TRAIL, mediated by inhibition of the NF-{kappa}B signaling pathway.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Jan;10(1):198-208. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0725. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21220502 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations Enhancing Selectivity of Antitumor Cytokine TRAIL to DR5 Receptor Increase Its Cytotoxicity against Tumor Cells.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2015 Aug;80(8):1080-91. doi: 10.1134/S0006297915080143. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2015. PMID: 26547077
-
Targeting pro-apoptotic trail receptors sensitizes HeLa cervical cancer cells to irradiation-induced apoptosis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008 Oct 1;72(2):543-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1902. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 18793956
-
Control of apoptosis signaling by Apo2 ligand.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1999;54:225-34. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1999. PMID: 10548878 Review.
-
Targeting death receptors for TRAIL by agents designed by Mother Nature.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Oct;35(10):520-36. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25128958 Review.
Cited by
-
TRAILblazing Strategies for Cancer Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 30;11(4):456. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040456. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30935038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of N-myc expression sensitizes human neuroblastoma IMR-32 cells expressing caspase-8 to TRAIL.Cell Prolif. 2019 May;52(3):e12577. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12577. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30724400 Free PMC article.
-
The essential role of TAp73 in bortezomib-induced apoptosis in p53-deficient colorectal cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 14;7(1):5423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05813-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28710427 Free PMC article.
-
Chemically modified liposomes carrying TRAIL target activated hepatic stellate cells and ameliorate hepatic fibrosis in vitro and in vivo.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Mar;23(3):1951-1962. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14097. Epub 2018 Dec 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30592139 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapeutic Agents Sensitize Resistant Cancer Cells to the DR5-Specific Variant DR5-B more Efficiently than to TRAIL by Modulating the Surface Expression of Death and Decoy Receptors.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 30;12(5):1129. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051129. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32365976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LeBlanc HN, Ashkenazi A (2003) Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ 10: 66–75. - PubMed
-
- Hymowitz SG, O'Connell MP, Ultsch MH, Hurst A, Totpal K, et al. (2000) A unique zinc-binding site revealed by a high-resolution X-ray structure of homotrimeric Apo2L/TRAIL. Biochemistry 39: 633–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

