Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in corticosteroid insensitivity of chronic oxidant lung injury
- PMID: 25310910
- PMCID: PMC4266539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.003
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in corticosteroid insensitivity of chronic oxidant lung injury
Abstract
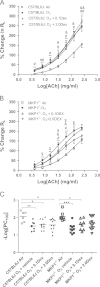
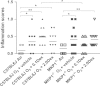
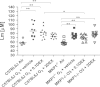
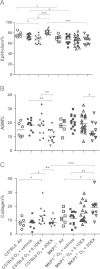
Oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and in the induction of corticosteroid (CS) insensitivity. Chronic ozone exposure leads to a model of COPD with lung inflammation and emphysema. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) may underlie CS insensitivity in COPD. We determined the role played by MKP-1 by studying the effect of corticosteroids in wild-type C57/BL6J and MKP-1(-/-) mice after chronic ozone exposure. Mice were exposed to ozone (3 ppm, 3 h) 12 times over 6 weeks. Dexamethasone (0.1 or 2 mg/kg; intraperitoneally) was administered before each exposure. Mice were studied 24 h after final exposure. In ozone-exposed C57/BL6J mice, bronchial hyperresponsiveness (BHR) was not inhibited by both doses of dexamethasone, but in MKP-1(-/-) mice, there was a small inhibition by high dose dexamethasone (2 mg/kg). There was an increase in mean linear intercept after chronic ozone exposure in both strains which was CS-insensitive. There was lesser inflammation after low dose of dexamethasone in MKP-1(-/-) mice compared to C57/Bl6J mice. Epithelial and collagen areas were modulated in ozone-exposed MKP-1(-/-) mice treated with dexamethasone compared to C57/Bl6J mice. MKP-1 regulated the expression of MMP-12, IL-13 and KC induced by ozone but did not alter dexamethasone׳s effects. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness, lung inflammation and emphySEMa after chronic exposure are CS-insensitive, and the contribution of MKP-1 to CS sensitivity in this model was negligible.
Keywords: Bronchial hyperresponsiveness; Emphysema; Lung inflammation; Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1); Ozone exposure.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of p38 MAPK-dependent bronchial contraction after ozone by corticosteroids.Eur Respir J. 2011 Apr;37(4):933-42. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00021110. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Eur Respir J. 2011. PMID: 20693246 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A modulates oxidant stress-induced airway hyperresponsiveness but not emphysema.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58452. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058452. Epub 2013 Mar 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505509 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in ovalbumin and ozone-induced mouse model of asthma.Respirology. 2013 Nov;18 Suppl 3:20-9. doi: 10.1111/resp.12189. Respirology. 2013. PMID: 24188200
-
Impact of ozone exposure on the response to glucocorticoid in a mouse model of asthma: involvements of p38 MAPK and MKP-1.Respir Res. 2014 Oct 8;15(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0126-x. Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 25287866 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress in Ozone-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Emphysema: A Facet of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 2;11:1957. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01957. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983127 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small-Airway Dysfunction is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Asthma: Evidence from Two Mouse Models.J Asthma Allergy. 2021 Jul 12;14:883-896. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S312361. eCollection 2021. J Asthma Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34285515 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptotanshinone Reverses Corticosteroid Insensitivity by Inhibition of Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase-δ in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 May 6;18:797-809. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S405757. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37180749 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Roles for RGS2 in a Mouse Model of House Dust Mite-Induced Airway Inflammation.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 20;12(1):e0170269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170269. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28107494 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 1 in Glucocorticoid-Driven Anti-inflammatory Responses.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01446. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31316508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role and regulation of MKP-1 in airway inflammation.Respir Res. 2017 Aug 10;18(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0637-3. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 28797290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adcock I.M., Ford P.A., Bhavsar P., Ahmad T., Chung K.F. Steroid resistance in asthma: mechanisms and treatment options. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008;8:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Bhavsar P., Hew M., Khorasani N., Torrego A., Barnes P.J., Adcock I., Chung K.F. Relative corticosteroid insensitivity of alveolar macrophages in severe asthma compared with non-severe asthma. Thorax. 2008;63:784–790. - PubMed
-
- Camps M., Nichols A., Arkinstall S. Dual specificity phosphatases: a gene family for control of MAP kinase function. FASEB J. 2000;14:6–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

