Role of in vivo vascular redox in resistance arteries
- PMID: 25312439
- PMCID: PMC4268237
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04473
Role of in vivo vascular redox in resistance arteries
Abstract
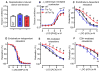
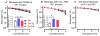
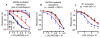
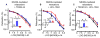
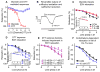
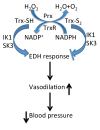
Vascular thiol redox state has been shown to modulate vasodilator functions in large conductance Ca2+ -activated K+ channels and other related channels. However, the role of vascular redox in small resistance arteries is unknown. To determine how in vivo modulation of thiol redox state affects small resistance arteries relaxation, we generated a transgenic mouse strain that overexpresses thioredoxin, a small redox protein (Trx-Tg), and another strain that is thioredoxin-deficient (dnTrx-Tg). The redox state of the mesenteric arteries (MAs) in Trx-Tg mice is found to be predominantly in reduced state; in contrast, MAs from dnTrx-Tg mice remain in oxidized state. Thus, we created an in vivo redox system of mice and isolated the second-order branches of the main superior MAs from wild-type, Trx-Tg, or dnTrx-Tg mice to assess endothelium-dependent relaxing responses in a wire myograph. In MAs isolated from Trx-Tg mice, we observed an enhanced intermediate-conductance Ca2+ -activated potassium channel contribution resulting in a larger endothelium-dependent hyperpolarizing (EDH) relaxation in response to indirect (acetylcholine) and direct (NS309) opening of endothelial calcium-activated potassium channels. MAs derived from dnTrx-Tg mice showed both blunted nitric oxide-mediated and EDH-mediated relaxation compared with Trx-Tg mice. In a control study, diamide decreased EDH relaxations in MAs of wild-type mice, whereas dithiothreitol improved EDH relaxations and was able to restore the diamide-induced impairment in EDH response. Furthermore, the basal or angiotensin II-mediated systolic blood pressure remained significantly lower in Trx-Tg mice compared with wild-type or dnTrx-Tg mice, thus directly establishing redox-mediated EDH in blood pressure control.
Keywords: endothelium; mesenteric arteries; relaxation; thioredoxins.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
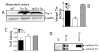

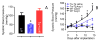
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Endothelial Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 4 Channel and Small-Conductance of Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels Underpins Impaired Endothelium-Dependent Hyperpolarization in Hypertension.Hypertension. 2017 Jan;69(1):143-153. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07110. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 27872234
-
Type 2 diabetes: increased expression and contribution of IKCa channels to vasodilation in small mesenteric arteries of ZDF rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):H1093-102. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00240.2013. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25128173
-
Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 potentiates EDH-type relaxations in the mesenteric artery of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Nov 15;305(10):H1471-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00962.2012. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24014672
-
Endothelium-Dependent Hyperpolarization (EDH) in Hypertension: The Role of Endothelial Ion Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 21;19(1):315. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010315. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29361737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization: age, gender and blood pressure, do they matter?Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017 Jan;219(1):108-123. doi: 10.1111/apha.12628. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017. PMID: 26548576 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase 4D promotes angiotensin II-induced hypertension in mice via smooth muscle cell contraction.Commun Biol. 2022 Jan 20;5(1):81. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03029-0. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35058564 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin deficiency exacerbates vascular dysfunction during diet-induced obesity in small mesenteric artery in mice.Microcirculation. 2021 May;28(4):e12674. doi: 10.1111/micc.12674. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Microcirculation. 2021. PMID: 33316843 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased EDHF-mediated relaxation is a major mechanism in endothelial dysfunction in resistance arteries in aged mice on prolonged high-fat sucrose diet.Physiol Rep. 2017 Dec;5(23):e13502. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13502. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29212858 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Regulation of K+ Channel: Role of Thioredoxin.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024 Nov;41(13-15):818-844. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0416. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024. PMID: 39099341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thioredoxin reverses age-related hypertension by chronically improving vascular redox and restoring eNOS function.Sci Transl Med. 2017 Feb 8;9(376):eaaf6094. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf6094. Sci Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28179506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas SR, Witting PK, Drummond GR. Redox control of endothelial function and dysfunction: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10:1713–1765. - PubMed
-
- Vanhoutte PM, Shimokawa H, Tang EH, Feletou M. Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2009;196:193–222. - PubMed
-
- Shimokawa H, Yasutake H, Fujii K, Owada MK, Nakaike R, Fukumoto Y, Takayanagi T, Nagao T, Egashira K, Fujishima M, Takeshita A. The importance of the hyperpolarizing mechanism increases as the vessel size decreases in endothelium-dependent relaxations in rat mesenteric circulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1996;28:703–711. - PubMed
-
- Hilgers RH, Todd J, Jr, Webb RC. Regional heterogeneity in acetylcholine-induced relaxation in rat vascular bed: Role of calcium-activated k+ channels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;291:H216–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

