Bipotential adult liver progenitors are derived from chronically injured mature hepatocytes
- PMID: 25312494
- PMCID: PMC4254170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.09.008
Bipotential adult liver progenitors are derived from chronically injured mature hepatocytes
Abstract
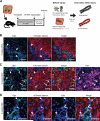
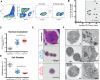
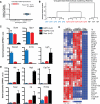
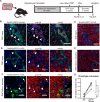
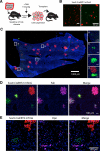
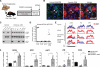
Adult liver progenitor cells are biliary-like epithelial cells that emerge only under injury conditions in the periportal region of the liver. They exhibit phenotypes of both hepatocytes and bile ducts. However, their origin and their significance to injury repair remain unclear. Here, we used a chimeric lineage tracing system to demonstrate that hepatocytes contribute to the progenitor pool. RNA-sequencing, ultrastructural analysis, and in vitro progenitor assays revealed that hepatocyte-derived progenitors were distinct from their biliary-derived counterparts. In vivo lineage tracing and serial transplantation assays showed that hepatocyte-derived proliferative ducts retained a memory of their origin and differentiated back into hepatocytes upon cessation of injury. Similarly, human hepatocytes in chimeric mice also gave rise to biliary progenitors in vivo. We conclude that human and mouse hepatocytes can undergo reversible ductal metaplasia in response to injury, expand as ducts, and subsequently contribute to restoration of the hepatocyte mass.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Regenerative biology: The versatile and plastic liver.Nature. 2015 Jan 8;517(7533):155-6. doi: 10.1038/517155a. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25567279 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alison MR, Golding M, Sarraf CE, Edwards RJ, Lalani EN. Liver damage in the rat induces hepatocyte stem cells from biliary epithelial cells. Ygast. 1996;110:1182–1190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

