Phenomics of Vascular Disease: The Systematic Approach to the Combination Therapy
- PMID: 25313004
- PMCID: PMC4397150
- DOI: 10.2174/1570161112666141014144829
Phenomics of Vascular Disease: The Systematic Approach to the Combination Therapy
Abstract
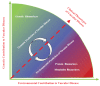
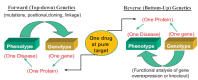
Vascular diseases are usually caused by multifactorial pathogeneses involving genetic and environmental factors. Our current understanding of vascular disease is, however, based on the focused genotype/phenotype studies driven by the "one-gene/one-phenotype" hypothesis. Drugs with "pure target" at individual molecules involved in the pathophysiological pathways are the mainstream of current clinical treatments and the basis of combination therapy of vascular diseases. Recently, the combination of genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics has unraveled the etiology and pathophysiology of vascular disease in a big-data fashion and also revealed unmatched relationships between the omic variability and the much narrower definition of various clinical phenotypes of vascular disease in individual patients. Here, we introduce the phenomics strategy that will change the conventional focused phenotype/genotype/genome study to a new systematic phenome/genome/proteome approach to the understanding of pathophysiology and combination therapy of vascular disease. A phenome is the sum total of an organism's phenotypic traits that signify the expression of genome and specific environmental influence. Phenomics is the study of phenome to quantitatively correlate complex traits to variability not only in genome, but also in transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, interactome, and environmental factors by exploring the systems biology that links the genomic and phenomic spaces. The application of phenomics and the phenome-wide associated study (PheWAS) will not only identify a systemically-integrated set of biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of vascular disease but also provide novel treatment targets for combination therapy and thus make a revolutionary paradigm shift in the clinical treatment of these devastating diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Iacoviello L., Donati M.B. Gene-environment interactions: implications for cardiovascular disease. Cardiologia. 1999;44:227–232. - PubMed
-
- Nordon I., Brar R., Hinchliffe R., Cockerill G., Loftus I., Thompson M. The role of proteomic research in vascular disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009;49:1602–1612. - PubMed
-
- Rafter N., Connor J., Hall J., et al. Cardiovascular medications in primary care: treatment gaps and targeting by absolute risk. N. Z. Med. J. 2005;118:U1676. - PubMed
-
- Weir M.R. Targeting mechanisms of hypertensive vascular disease with dual calcium channel and renin-angiotensin system blockade. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2007;21:770–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

