Assessment of breast pathologies using nonlinear microscopy
- PMID: 25313045
- PMCID: PMC4217415
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1416955111
Assessment of breast pathologies using nonlinear microscopy
Abstract
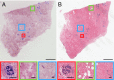
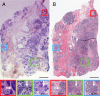
Rapid intraoperative assessment of breast excision specimens is clinically important because up to 40% of patients undergoing breast-conserving cancer surgery require reexcision for positive or close margins. We demonstrate nonlinear microscopy (NLM) for the assessment of benign and malignant breast pathologies in fresh surgical specimens. A total of 179 specimens from 50 patients was imaged with NLM using rapid extrinsic nuclear staining with acridine orange and intrinsic second harmonic contrast generation from collagen. Imaging was performed on fresh, intact specimens without the need for fixation, embedding, and sectioning required for conventional histopathology. A visualization method to aid pathological interpretation is presented that maps NLM contrast from two-photon fluorescence and second harmonic signals to features closely resembling histopathology using hematoxylin and eosin staining. Mosaicking is used to overcome trade-offs between resolution and field of view, enabling imaging of subcellular features over square-centimeter specimens. After NLM examination, specimens were processed for standard paraffin-embedded histology using a protocol that coregistered histological sections to NLM images for paired assessment. Blinded NLM reading by three pathologists achieved 95.4% sensitivity and 93.3% specificity, compared with paraffin-embedded histology, for identifying invasive cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ versus benign breast tissue. Interobserver agreement was κ = 0.88 for NLM and κ = 0.89 for histology. These results show that NLM achieves high diagnostic accuracy, can be rapidly performed on unfixed specimens, and is a promising method for intraoperative margin assessment.
Keywords: breast cancer; imaging; nonlinear microscopy; pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American Cancer Society . Global Cancer Facts & Figures. 2nd Ed American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2011.
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2012. American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2012.
-
- Fisher B, et al. Eight-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1989;320(13):822–828. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, et al. Reanalysis and results after 12 years of follow-up in a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy with lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(22):1456–1461. - PubMed
-
- Nesvold IL, Dahl AA, Løkkevik E, Marit Mengshoel A, Fosså SD. Arm and shoulder morbidity in breast cancer patients after breast-conserving therapy versus mastectomy. Acta Oncol. 2008;47(5):835–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

