Open TG-GATEs: a large-scale toxicogenomics database
- PMID: 25313160
- PMCID: PMC4384023
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku955
Open TG-GATEs: a large-scale toxicogenomics database
Abstract
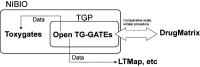
Toxicogenomics focuses on assessing the safety of compounds using gene expression profiles. Gene expression signatures from large toxicogenomics databases are expected to perform better than small databases in identifying biomarkers for the prediction and evaluation of drug safety based on a compound's toxicological mechanisms in animal target organs. Over the past 10 years, the Japanese Toxicogenomics Project consortium (TGP) has been developing a large-scale toxicogenomics database consisting of data from 170 compounds (mostly drugs) with the aim of improving and enhancing drug safety assessment. Most of the data generated by the project (e.g. gene expression, pathology, lot number) are freely available to the public via Open TG-GATEs (Toxicogenomics Project-Genomics Assisted Toxicity Evaluation System). Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of the database, including both gene expression data and metadata, with a description of experimental conditions and procedures used to generate the database. Open TG-GATEs is available from http://toxico.nibio.go.jp/english/index.html.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

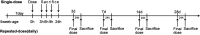
Similar articles
-
Systems toxicology of chemically induced liver and kidney injuries: histopathology-associated gene co-expression modules.J Appl Toxicol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1137-49. doi: 10.1002/jat.3278. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Appl Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26725466 Free PMC article.
-
LTMap: a web server for assessing the potential liver toxicity by genome-wide transcriptional expression data.J Appl Toxicol. 2014 Jul;34(7):805-9. doi: 10.1002/jat.2923. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Appl Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24022982
-
Predicting drug-induced hepatotoxicity using QSAR and toxicogenomics approaches.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Aug 15;24(8):1251-62. doi: 10.1021/tx200148a. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21699217 Free PMC article.
-
A decade of toxicogenomic research and its contribution to toxicological science.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Dec;130(2):217-28. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs223. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22790972 Review.
-
Large-scale databases in toxicogenomics.Pharmacogenomics. 2005 Oct;6(7):749-54. doi: 10.2217/14622416.6.7.749. Pharmacogenomics. 2005. PMID: 16207151 Review.
Cited by
-
WERFE: A Gene Selection Algorithm Based on Recursive Feature Elimination and Ensemble Strategy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 May 28;8:496. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00496. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32548100 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Switches 'on' MAPK and NFκB Signaling via the Reduction of Nuclear DUSP1 and DUSP5 Expression.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 20;12:631879. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.631879. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995033 Free PMC article.
-
Research Resource: A Reference Transcriptome for Constitutive Androstane Receptor and Pregnane X Receptor Xenobiotic Signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Aug;30(8):937-48. doi: 10.1210/me.2016-1095. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27409825 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Adverse Outcome Pathways, Causal Networks and 'Omics to Support Chemical Hazard Assessment.Front Toxicol. 2022 Mar 24;4:786057. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.786057. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35399296 Free PMC article.
-
Mining Public Toxicogenomic Data Reveals Insights and Challenges in Delineating Liver Steatosis Adverse Outcome Pathways.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 18;10:1007. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01007. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31681434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urushidani T. Prediction of hepatotoxicity based on the toxicogenomics database. In: Sahu SC, editor. Hepatotoxicity: From Genomics to In Vitro and In Vivo Models. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; 2007. pp. 507–529.
-
- Kondo C., Minowa Y., Uehara T., Okuno Y., Nakatsu N., Ono A., Maruyama T., Kato I., Yamate J., Yamada H., et al. Identification of genomic biomarkers for concurrent diagnosis of drug-induced renal tubular injury using a large-scale toxicogenomics database. Toxicology. 2009;265:15–26. - PubMed
-
- Gao W., Mizukawa Y., Nakatsu N., Minowa Y., Yamada H., Ohno Y., Urushidani T. Mechanism-based biomarker gene sets for glutathione depletion-related hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010;247:211–221. - PubMed
-
- Uehara T., Minowa Y., Morikawa Y., Kondo C., Maruyama T., Kato I., Nakatsu N., Igarashi Y., Ono A., Hayashi H., et al. Prediction model of potential hepatocarcinogenicity of rat hepatocarcinogens using a large-scale toxicogenomics database. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011;255:297–306. - PubMed
-
- Minowa Y., Kondo C., Uehara T., Morikawa Y., Okuno Y., Nakatsu N., Ono A., Maruyama T., Kato I., Yamate J., et al. Toxicogenomic multigene biomarker for predicting the future onset of proximal tubular injury in rats. Toxicology. 2012;297:47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

