Genetic, psychosocial and clinical factors associated with hippocampal volume in the general population
- PMID: 25313508
- PMCID: PMC4350511
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2014.102
Genetic, psychosocial and clinical factors associated with hippocampal volume in the general population
Abstract
The hippocampus--crucial for memory formation, recall and mood regulation--is involved in the pathophysiology of dementia and depressive disorders. Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified five genetic loci associated with hippocampal volume (HV). Previous studies have described psychosocial and clinical factors (for example, smoking, type 2 diabetes and hypertension) to have an impact on HV. However, the interplay between genetic, psychosocial and clinical factors on the HV remains unclear. Still, it is likely that genetic variants and clinical or psychosocial factors jointly act in modifying HV; it might be possible they even interact. Knowledge of these factors might help to quantify ones individual risk of or rather resilience against HV loss. We investigated subjects (N=2463; 55.7% women; mean age 53 years) from the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP-2; SHIP-TREND-0) who underwent whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and genotyping. HVs were estimated with FreeSurfer. For optimal nonlinear model fitting, we used regression analyses with restricted cubic splines. Genetic variants and associated psychosocial or clinical factors were jointly assessed for potential two-way interactions. We observed associations between HV and gender (P<0.0001), age (P<0.0001), body height (P<0.0001), education (P=0.0053), smoking (P=0.0058), diastolic blood pressure (P=0.0211), rs7294919 (P=0.0065), rs17178006 (P=0.0002), rs6581612 (P=0.0036), rs6741949 (P=0.0112) and rs7852872 (P=0.0451). In addition, we found three significant interactions: between rs7294919 and smoking (P=0.0473), rs7294919 and diastolic blood pressure (P=0.0447) and between rs7852872 and rs6581612 (P=0.0114). We suggest that these factors might have a role in the individual susceptibility to hippocampus-associated disorders.
Figures

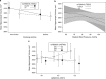
References
-
- Burgess N, Maguire EA, O'Keefe J. The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron. 2002;35:625–641. - PubMed
-
- Szeszko PR, Strous RD, Goldman RS, Ashtari M, Knuth KH, Lieberman JA, et al. Neuropsychological correlates of hippocampal volumes in patients experiencing a first episode of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159:217–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

