MicroRNA-223-3p inhibits the angiogenesis of ischemic cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via affecting RPS6KB1/hif-1a signal pathway
- PMID: 25313822
- PMCID: PMC4196764
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108468
MicroRNA-223-3p inhibits the angiogenesis of ischemic cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via affecting RPS6KB1/hif-1a signal pathway
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a recently discovered class of posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression with critical functions in the angiogenesis and cardiovascular diseases; however, the details of miRNAs regulating mechanism of angiogenesis of ischemic cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs) are not yet reported.
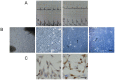
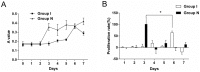
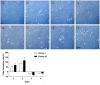
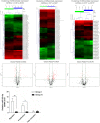
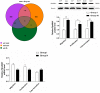
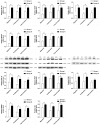
Methods and results: This study analyzes the changes of the dynamic expression of miRNAs during the process of angiogenesis of ischemic CMECs by applying miRNA chip and real-time PCR for the first time. Compared with normal CMECs, ischemic CMECs have a specific miRNAs expression profile, in which mir-223-3p has the most significant up-regulation, especially during the process of migration and proliferation, while the up-regulation is the most significant during migration, reaching 11.02 times. Rps6kb1 is identified as a potential direct and functional target of mir-223-3p by applying bioinformatic prediction, real-time PCR and Western blot. Pathway analysis report indicates Rps6kb1 regulates the angiogenesis by participating into hif-1a signal pathway. Further analysis reveals that both the gene and protein expression of the downstream molecules VEGF, MAPK, PI3K and Akt of Rps6kb1/hif-1a signal pathway decrease significantly during the process of migration and proliferation in the ischemic CMECs. Therefore, it is confirmed that mir-223-3p inhibits the angiogenesis of CMECs, at least partly, via intervening RPS6KB1/hif-1a signal pathway and affecting the process of migration and proliferation.
Conclusion: This study elucidates the miRNA regulating law in the angiogenesis of CMECs; mir-223-3p inhibits the process of migration and proliferation of ischemic CMECs probably via affecting RPS6KB1/hif-1a signal pathway, which in turn suppresses the angiogenesis. It is highly possible that mir-223-3p becomes a novel intervention core target in the treatment of angiogenesis of ischemic heart diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight. Nat Rev Genet 9 2: 102–114. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Ceel 120 1: 15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

