Onecut1 and Onecut2 play critical roles in the development of the mouse retina
- PMID: 25313862
- PMCID: PMC4196951
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110194
Onecut1 and Onecut2 play critical roles in the development of the mouse retina
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115786
Abstract
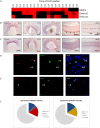
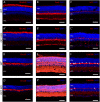
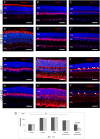
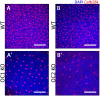
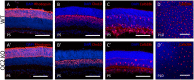
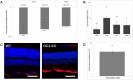
The entire repertoire of intrinsic factors that control the cell fate determination process of specific retinal neurons has yet to be fully identified. Single cell transcriptome profiling experiments of retinal progenitor cells revealed considerable gene expression heterogeneity between individual cells, especially among different classes of transcription factors. In this study, we show that two of those factors, Onecut1 and Onecut2, are expressed during mouse retinal development. Using mice that are deficient for each of these transcription factors, we further demonstrate a significant loss (∼70-80%) of horizontal cells in the absence of either of these proteins, while the other retinal cells appear at normal numbers. Microarray profiling experiments performed on knockout retinas revealed defects in horizontal cell genes as early as E14.5. Additional profiling assays showed an upregulation of several stress response genes in the adult Onecut2 knockout, suggesting that the integrity of the retina is compromised in the absence of normal numbers of horizontal cells. Interestingly, melanopsin, the gene coding for the photopigment found in photosensitive ganglion cells, was observed to be upregulated in Onecut1 deficient retinas, pointing to a possible regulatory role for Onecut1. Taken together, our data show that similar to Onecut1, Onecut2 is also necessary for the formation of normal numbers of horizontal cells in the developing retina.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Edlund T, Jessell TM (1999) Progression from extrinsic to intrinsic signaling in cell fate specification: a view from the nervous system. Cell 96: 211–224. - PubMed
-
- Goetz JJ, Farris C, Chowdhury R, Trimarchi JM (2014) Making of a Retinal Cell. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology. Elsevier, Vol. 308: 273–321 Available: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128000977000075 Accessed 12 May 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

