Drug delivery to the malaria parasite using an arterolane-like scaffold
- PMID: 25314098
- PMCID: PMC4420023
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201402362
Drug delivery to the malaria parasite using an arterolane-like scaffold
Abstract
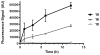
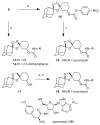
Antimalarial agents artemisinin and arterolane act via initial reduction of a peroxide bond in a process likely mediated by ferrous iron sources in the parasite. Here, we report the synthesis and antiplasmodial activity of arterolane-like 1,2,4-trioxolanes specifically designed to release a tethered drug species within the malaria parasite. Compared with our earlier drug delivery scaffolds, these new arterolane-inspired systems are of significantly decreased molecular weight and possess superior metabolic stability. We describe an efficient, concise and scalable synthesis of the new systems, and demonstrate the use of the aminonucleoside antibiotic puromycin as a chemo/biomarker to validate successful drug release in live Plasmodium falciparum parasites. Together, the improved drug-like properties, more efficient synthesis, and proof of concept using puromycin, suggests these new molecules as improved vehicles for targeted drug delivery to the malaria parasite.
Keywords: Plasmodium falciparum; antimalarial agents; drug delivery; puromycin; targeted prodrugs; trioxolanes.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
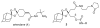

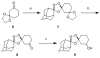
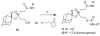
References
-
- Vennerstrom JL, Arbe-Barnes S, Brun R, Charman SA, Chiu FCK, Chollet J, Dong Y, Dorn A, Hunziker D, Matile H, et al. Nature. 2004;430:900–904. - PubMed
-
- Dong Y, Wittlin S, Sriraghavan K, Chollet J, Charman SA, Charman WN, Scheurer C, Urwyler H, Santo Tomas J, Snyder C, et al. J Med Chem. 2010;53:481–91. - PubMed
-
- Marti F, Chadwick J, Amewu RK, Burrell-Saward H, Srivastava A, Ward Sa, Sharma R, Berry N, O’Neill PM. Medchemcomm. 2011;2:661.
-
- O’Neill PM, Posner GH. J Med Chem. 2004;47:2945–2964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

