Development and customization of a color-coded microbeads-based assay for drug resistance in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase
- PMID: 25314293
- PMCID: PMC4196989
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109823
Development and customization of a color-coded microbeads-based assay for drug resistance in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase
Abstract
Background: Drug resistance (DR) of HIV-1 can be examined genotypically or phenotypically. Although sequencing is the gold standard of the genotypic resistance testing (GRT), high-throughput GRT targeted to the codons responsible for DR may be more appropriate for epidemiological studies and public health research.
Methods: We used a Japanese database to design and synthesize sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes (SSOP) for the detection of wild-type sequences and 6 DR mutations in the clade B HIV-1 reverse transcriptase region. We coupled SSOP to microbeads of the Luminex 100 xMAP system and developed a GRT based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-SSOP-Luminex method.
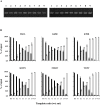
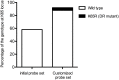
Results: Sixteen oligoprobes for discriminating DR mutations from wild-type sequences at 6 loci were designed and synthesized, and their sensitivity and specificity were confirmed using isogenic plasmids. The PCR-SSOP-Luminex DR assay was then compared to direct sequencing using 74 plasma specimens from treatment-naïve patients or those on failing treatment. In the majority of specimens, the results of the PCR-SSOP-Luminex DR assay were concordant with sequencing results: 62/74 (83.8%) for M41, 43/74 (58.1%) for K65, 70/74 (94.6%) for K70, 55/73 (75.3%) for K103, 63/73 (86.3%) for M184 and 68/73 (93.2%) for T215. There were a number of specimens without any positive signals, especially for K65. The nucleotide position of A2723G, A2747G and C2750T were frequent polymorphisms for the wild-type amino acids K65, K66 and D67, respectively, and 14 specimens had the D67N mutation encoded by G2748A. We synthesized 14 additional oligoprobes for K65, and the sensitivity for K65 loci improved from 43/74 (58.1%) to 68/74 (91.9%).
Conclusions: We developed a rapid high-throughput assay for clade B HIV-1 DR mutations, which could be customized by synthesizing oligoprobes suitable for the circulating viruses. The assay could be a useful tool especially for public health research in both resource-rich and resource-limited settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Palella FJ Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, et al. (1998) Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 338: 853–860. - PubMed
-
- Frentz D, Boucher CA, van de Vijver DA (2012) Temporal changes in the epidemiology of transmission of drug-resistant HIV-1 across the world. AIDS Rev 14: 17–27. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2012) WHO HIV Drug Resistance Report 2012. WHO Press.
-
- WHO (2013) Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: Recommendations for a public health approach. WHO Press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

