Improvement of radiotherapy-induced lacrimal gland injury by induced pluripotent stem cell-derived conditioned medium via MDK and inhibition of the p38/JNK pathway
- PMID: 25314301
- PMCID: PMC4227222
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms151018407
Improvement of radiotherapy-induced lacrimal gland injury by induced pluripotent stem cell-derived conditioned medium via MDK and inhibition of the p38/JNK pathway
Abstract
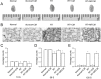
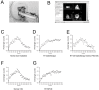
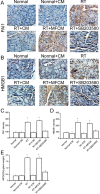
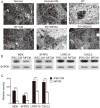
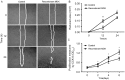
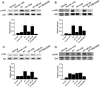
Radiation therapy is the most widely used and effective treatment for orbital tumors, but it causes dry eye due to lacrimal gland damage. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived conditioned medium (iPSC-CM) has been shown to rescue different types of tissue damage. The present study investigated the mechanism of the potential radioprotective effect of IPS cell-derived conditioned medium (iPSC-CM) on gamma-irradiation-induced lacrimal gland injury (RILI) in experimental mice. In this study, we found that iPSC-CM ameliorated RILI. iPSC-CM markedly decreased radiotherapy induced inflammatory processes, predominantly through suppressing p38/JNK signaling. Further signaling pathway analyses indicated that iPSC-CM could suppress Akt (Protein Kinase B, PKB) phosphorylation. High levels of midkine (MDK) were also found in iPSC-CM and could be involved in lacrimal gland regeneration by promoting cell migration and proliferation. Thus, our study indicates that inhibiting the p38/JNK pathway or increasing the MDK level might be a therapeutic target for radiation-induced lacrimal gland injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiotherapy‑induced Gadd45a impairs lacrimal gland epithelial cell migration and proliferation.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Oct;8(4):1049-54. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1636. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 23969889
-
Improvement of ventilator-induced lung injury by IPS cell-derived conditioned medium via inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway and IP-10-dependent paracrine regulation.Biomaterials. 2013 Jan;34(1):78-91. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.042. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23063297
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury by Downregulating the Oxidative Stress-Related Pathway in Ischemia-Reperfusion Rats.Cell Transplant. 2016;25(3):517-30. doi: 10.3727/096368915X688542. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Cell Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26132529
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Alveolar Epithelial Cells under Septic Conditions In Vitro via the JNK-P38 Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(5):1830-46. doi: 10.1159/000438545. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26584283
-
The role of stress-activated protein kinase signaling in renal pathophysiology.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2009 Jan;42(1):29-37. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2008005000049. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2009. PMID: 18982195 Review.
Cited by
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell-conditional medium inhibits H9C2 cardiomyocytes apoptosis via autophagy flux and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jun;23(6):4358-4374. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14327. Epub 2019 Apr 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30957422 Free PMC article.
-
Enterovirus A71 infection-induced dry eye-like symptoms by damaging the lacrimal glands.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Apr 2;14:1340075. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1340075. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38628549 Free PMC article.
-
Newer approaches to dry eye therapy: Nanotechnology, regenerative medicine, and tissue engineering.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;71(4):1292-1303. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2806_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37026261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current approaches for the regeneration and reconstruction of ocular surface in dry eye.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 23;9:885780. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.885780. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36213677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of induced pluripotent stem cells-derived conditioned medium on the proliferation and anti-apoptosis of human adipose-derived stem cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Feb;413(1-2):69-85. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2640-7. Epub 2016 Jan 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26724952
References
-
- Parsons J.T., Bova F.J., Fitzgerald C.R., Mendenhall W.M., Million R.R. Severe dry-eye syndrome following external beam irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994;30:775–780. - PubMed
-
- Parsons J.T., Bova F.J., Mendenhall W.M., Million R.R., Fitzgerald C.R. Response of the normal eye to high dose radiotherapy. Oncology. 1996;10:837–847. - PubMed
-
- Horwath-Winter J., Schneider M.R., Wackernagel W., Rabensteiner D., Boldin I., Haller-Schober E.M., Langmann G. Influence of single-fraction gamma-knife radiosurgery on ocular surface and tear function in choroidal melanoma patients. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013;97:466–470. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2012-302402. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Solans R., Bosch J.A., Galofre P., Porta F., Rosello J., Selva-O’Callagan A., Vilardell M. Salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction (sicca syndrome) after radioiodine therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2001;42:738–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

