Alveolar pentraxin 3 as an early marker of microbiologically confirmed pneumonia: a threshold-finding prospective observational study
- PMID: 25314919
- PMCID: PMC4219103
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-014-0562-5
Alveolar pentraxin 3 as an early marker of microbiologically confirmed pneumonia: a threshold-finding prospective observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Timely diagnosis of pneumonia in intubated critically ill patients is rather challenging. Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) is an acute-phase mediator produced by various cell types in the lungs. Animal studies have shown that, during pneumonia, PTX3 participates in fine-tuning of inflammation (for example, microbial clearance and recruitment of neutrophils). We previously described an association between alveolar PTX3 and lung infection in a small group of intubated patients. The aim of the present study was to determine a threshold level of alveolar PTX3 with elevated sensitivity and specificity for microbiologically confirmed pneumonia.
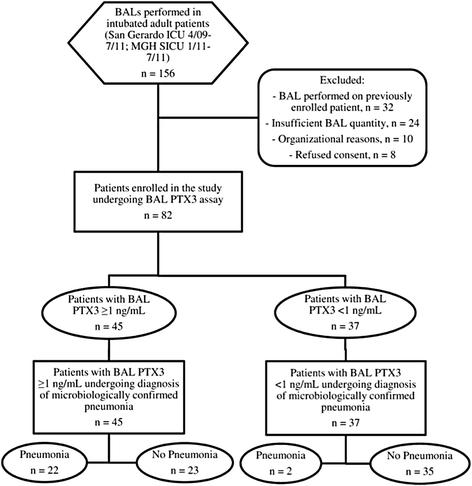
Methods: We recruited 82 intubated patients from two intensive care units (San Gerardo Hospital, Monza, Italy, and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA) undergoing bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) as per clinical decision. We collected BAL fluid and plasma samples, together with relevant clinical and microbiological data. We assayed PTX3 and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 (sTREM-1) in BAL fluid and PTX3, sTREM-1, C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) in plasma. Two blinded independent physicians reviewed patient data to confirm pneumonia. We determined the PTX3 threshold in BAL fluid for pneumonia and compared it to other biomarkers.
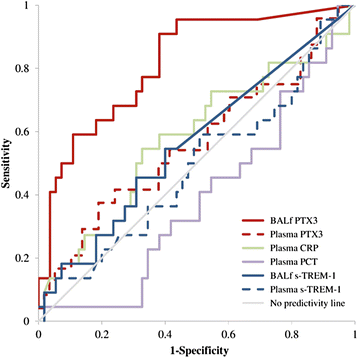
Results: Microbiologically confirmed pneumonia of bacterial (n =12), viral (n =4) or fungal (n =8) etiology was diagnosed in 24 patients (29%). PTX3 levels in BAL fluid predicted pneumonia with an area under the receiving operator curve of 0.815 (95% CI =0.710 to 0.921, P <0.0001), whereas none of the other biomarkers were effective. In particular, PTX3 levels ≥1 ng/ml in BAL fluid predicted pneumonia in univariate analysis (β =2.784, SE =0.792, P <0.001) with elevated sensitivity (92%), specificity (60%) and negative predictive value (95%). Net reclassification index PTX3 values ≥1 ng/ml in BAL fluid for pneumonia indicated gain in sensitivity and/or specificity vs. all other mediators. These results did not change when we limited our analyses only to confirmed cases of bacterial pneumonia. Moreover, when we considered only the 70 patients who fulfilled the clinical criteria for the diagnosis of pneumonia at BAL fluid sampling, the diagnostic accuracy of PTX levels was confirmed in univariate and ROC curve analysis.
Conclusions: In this hypothesis-generating convenience sample, a PTX3 level ≥1 ng/ml in BAL fluid was discriminative of microbiologically confirmed pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

