Ensemble learning of inverse probability weights for marginal structural modeling in large observational datasets
- PMID: 25316152
- PMCID: PMC4262745
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.6322
Ensemble learning of inverse probability weights for marginal structural modeling in large observational datasets
Abstract
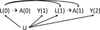
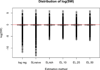
Inverse probability weights used to fit marginal structural models are typically estimated using logistic regression. However, a data-adaptive procedure may be able to better exploit information available in measured covariates. By combining predictions from multiple algorithms, ensemble learning offers an alternative to logistic regression modeling to further reduce bias in estimated marginal structural model parameters. We describe the application of two ensemble learning approaches to estimating stabilized weights: super learning (SL), an ensemble machine learning approach that relies on V-fold cross validation, and an ensemble learner (EL) that creates a single partition of the data into training and validation sets. Longitudinal data from two multicenter cohort studies in Spain (CoRIS and CoRIS-MD) were analyzed to estimate the mortality hazard ratio for initiation versus no initiation of combined antiretroviral therapy among HIV positive subjects. Both ensemble approaches produced hazard ratio estimates further away from the null, and with tighter confidence intervals, than logistic regression modeling. Computation time for EL was less than half that of SL. We conclude that ensemble learning using a library of diverse candidate algorithms offers an alternative to parametric modeling of inverse probability weights when fitting marginal structural models. With large datasets, EL provides a rich search over the solution space in less time than SL with comparable results.
Keywords: data-adaptive; ensemble learning; inverse probability weighting; longitudinal data; marginal structural model; super learning.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Estimating inverse probability weights using super learner when weight-model specification is unknown in a marginal structural Cox model context.Stat Med. 2017 Jun 15;36(13):2032-2047. doi: 10.1002/sim.7266. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Stat Med. 2017. PMID: 28219110
-
Super learning to hedge against incorrect inference from arbitrary parametric assumptions in marginal structural modeling.J Clin Epidemiol. 2013 Aug;66(8 Suppl):S99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.01.016. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23849160 Free PMC article.
-
Using marginal structural measurement-error models to estimate the long-term effect of antiretroviral therapy on incident AIDS or death.Am J Epidemiol. 2010 Jan 1;171(1):113-22. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp329. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Am J Epidemiol. 2010. PMID: 19934191 Free PMC article.
-
Causal models adjusting for time-varying confounding-a systematic review of the literature.Int J Epidemiol. 2019 Feb 1;48(1):254-265. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyy218. Int J Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 30358847
-
Stacked generalization: an introduction to super learning.Eur J Epidemiol. 2018 May;33(5):459-464. doi: 10.1007/s10654-018-0390-z. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Eur J Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29637384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Networks to Estimate Generalized Propensity Scores for Continuous Treatment Doses.Eval Rev. 2021 Feb-Apr;45(1-2):3-33. doi: 10.1177/0193841X21992199. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Eval Rev. 2021. PMID: 33653165 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparing the effectiveness of multiple dynamic treatment strategies using target trial emulation].Pravent Gesundh. 2023 Jun 12:1-11. doi: 10.1007/s11553-023-01033-8. Online ahead of print. Pravent Gesundh. 2023. PMID: 40479120 Free PMC article. German.
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Early Coronary Artery Disease Testing After New-Onset Heart Failure.Circ Heart Fail. 2023 Jul;16(7):e010426. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.122.010426. Epub 2023 May 22. Circ Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37212148 Free PMC article.
-
Causal inference as an emerging statistical approach in neurology: an example for epilepsy in the elderly.Clin Epidemiol. 2016 Dec 30;9:9-18. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S121023. eCollection 2017. Clin Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 28115873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Race, Ethnicity, Income Concentration and 10-Year Change in Urban Greenness in the United States.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Dec 10;14(12):1546. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14121546. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29232867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernan MA, Brumback B, Robins JM. Marginal structural models to estimate the causal effect of zidovudine on the survival of HIV-positive men. Epidemiology. 2000;11(5):561–570. - PubMed
-
- Neugebauer R, Chandra M, Paredes A, Graham D, McCloskey C, Go A. A marginal structural modeling approach with super learning for a study on oral bisphosphonate therapy and atrial fibrillation. Journal of Causal Inference. 2013;1:21–50.
-
- van der Laan M, Polley E, Hubbard A. Super Learner. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology. 2007;6(25) - PubMed
-
- Polley E, van der Laan M. Technical Report. Berkeley: Division of Biostatistics, University of California; 2010. Super learner in prediction.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
