Spatiotemporal Signatures of Lexical-Semantic Prediction
- PMID: 25316341
- PMCID: PMC4785937
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhu219
Spatiotemporal Signatures of Lexical-Semantic Prediction
Abstract
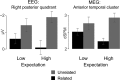
Although there is broad agreement that top-down expectations can facilitate lexical-semantic processing, the mechanisms driving these effects are still unclear. In particular, while previous electroencephalography (EEG) research has demonstrated a reduction in the N400 response to words in a supportive context, it is often challenging to dissociate facilitation due to bottom-up spreading activation from facilitation due to top-down expectations. The goal of the current study was to specifically determine the cortical areas associated with facilitation due to top-down prediction, using magnetoencephalography (MEG) recordings supplemented by EEG and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in a semantic priming paradigm. In order to modulate expectation processes while holding context constant, we manipulated the proportion of related pairs across 2 blocks (10 and 50% related). Event-related potential results demonstrated a larger N400 reduction when a related word was predicted, and MEG source localization of activity in this time-window (350-450 ms) localized the differential responses to left anterior temporal cortex. fMRI data from the same participants support the MEG localization, showing contextual facilitation in left anterior superior temporal gyrus for the high expectation block only. Together, these results provide strong evidence that facilitatory effects of lexical-semantic prediction on the electrophysiological response 350-450 ms postonset reflect modulation of activity in left anterior temporal cortex.
Keywords: N400; anterior temporal cortex; expectation; magnetoencephalography; semantic.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Automatic semantic facilitation in anterior temporal cortex revealed through multimodal neuroimaging.J Neurosci. 2013 Oct 23;33(43):17174-81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1018-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24155321 Free PMC article.
-
N400-like magnetoencephalography responses modulated by semantic context, word frequency, and lexical class in sentences.Neuroimage. 2002 Nov;17(3):1101-16. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2002.1268. Neuroimage. 2002. PMID: 12414253
-
Multimodal imaging of repetition priming: Using fMRI, MEG, and intracranial EEG to reveal spatiotemporal profiles of word processing.Neuroimage. 2010 Nov 1;53(2):707-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.069. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20620212 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for automatic sentence priming in the fusiform semantic area: convergent ERP and fMRI findings.Brain Res. 2008 Dec 3;1243:134-45. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.045. Epub 2008 Sep 24. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18840418
-
Neural localization of semantic context effects in electromagnetic and hemodynamic studies.Brain Lang. 2006 Jun;97(3):279-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Dec 15. Brain Lang. 2006. PMID: 16343606 Review.
Cited by
-
Language in Context: MEG Evidence for Modality-General and -Specific Responses to Reference Resolution.eNeuro. 2016 Dec 30;3(6):ENEURO.0145-16.2016. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0145-16.2016. eCollection 2016 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2016. PMID: 28058272 Free PMC article.
-
Semantic Processing in Healthy Aging and Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review of the N400 Differences.Brain Sci. 2020 Oct 23;10(11):770. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10110770. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33114051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction and error in early infant speech learning: A speech acquisition model.Cognition. 2021 Jul;212:104697. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104697. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Cognition. 2021. PMID: 33798952 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophysiological correlates of automatic integration of voice and gender information during grammatical processing.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 30;12(1):13114. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14478-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35908074 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal characterization of the semantic N400 response within a rapid evaluation brain vital sign framework.J Transl Med. 2018 Jun 4;16(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1527-2. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29866112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashby FG. 2011. Statistical analysis of fMRI data. Cambridge: (MA: ): MIT Press.
-
- Bodner GE, Masson ME. 2003. Beyond spreading activation: an influence of relatedness proportion on masked semantic priming. Psychon Bull Rev. 10(3):645–652. - PubMed
-
- Brennan J, Pylkkänen L. 2012. The time-course and spatial distribution of brain activity associated with sentence processing. Neuroimage. 60(2):1139–1148. - PubMed
-
- Brown CM, Hagoort P, Chwilla DJ. 2000. An event-related brain potential analysis of visual word priming effects. Brain Lang. 72(2):158–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

