Spatiotemporal Signatures of Lexical-Semantic Prediction
- PMID: 25316341
- PMCID: PMC4785937
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhu219
Spatiotemporal Signatures of Lexical-Semantic Prediction
Abstract
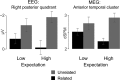
Although there is broad agreement that top-down expectations can facilitate lexical-semantic processing, the mechanisms driving these effects are still unclear. In particular, while previous electroencephalography (EEG) research has demonstrated a reduction in the N400 response to words in a supportive context, it is often challenging to dissociate facilitation due to bottom-up spreading activation from facilitation due to top-down expectations. The goal of the current study was to specifically determine the cortical areas associated with facilitation due to top-down prediction, using magnetoencephalography (MEG) recordings supplemented by EEG and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in a semantic priming paradigm. In order to modulate expectation processes while holding context constant, we manipulated the proportion of related pairs across 2 blocks (10 and 50% related). Event-related potential results demonstrated a larger N400 reduction when a related word was predicted, and MEG source localization of activity in this time-window (350-450 ms) localized the differential responses to left anterior temporal cortex. fMRI data from the same participants support the MEG localization, showing contextual facilitation in left anterior superior temporal gyrus for the high expectation block only. Together, these results provide strong evidence that facilitatory effects of lexical-semantic prediction on the electrophysiological response 350-450 ms postonset reflect modulation of activity in left anterior temporal cortex.
Keywords: N400; anterior temporal cortex; expectation; magnetoencephalography; semantic.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Ashby FG. 2011. Statistical analysis of fMRI data. Cambridge: (MA: ): MIT Press.
-
- Bodner GE, Masson ME. 2003. Beyond spreading activation: an influence of relatedness proportion on masked semantic priming. Psychon Bull Rev. 10(3):645–652. - PubMed
-
- Brennan J, Pylkkänen L. 2012. The time-course and spatial distribution of brain activity associated with sentence processing. Neuroimage. 60(2):1139–1148. - PubMed
-
- Brown CM, Hagoort P, Chwilla DJ. 2000. An event-related brain potential analysis of visual word priming effects. Brain Lang. 72(2):158–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

