A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of managing parotid and submandibular sialoliths using sialendoscopy assisted surgery
- PMID: 25316462
- PMCID: PMC4362127
A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of managing parotid and submandibular sialoliths using sialendoscopy assisted surgery
Abstract
Objectives: To review the available techniques and procedures for management of parotid and submandibular sialoliths with special emphasis on the efficacy and safety of the most commonly used combination of techniques; namely, sialendoscopy with conservative surgical removal of the stone.
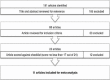
Methods: A systematic search of the English literature using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane library databases were conducted at the Faculty of Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Articles between the years 2004 and 2013 were selected on the basis of preset inclusion criteria. Then, they were reviewed against a checklist to assess the evidence of efficacy of therapy or prevention and analyzed for pertinent data.
Results: Eleven articles met the inclusion criteria and were reviewed and analyzed. The success rate of sialendoscopy combined with minor surgical removal of parotid and submandibular sialoliths ranges from 69-100%.
Conclusion: Sialendoscopy combined with a minor surgical extraction of parotid and submandibular sialoliths is safe and efficacious.
Figures

References
-
- Ngu RK, Brown JE, Whaites EJ, Drage NA, Ng SY, Makdissi J. Salivary duct strictures: nature and incidence in benign salivary obstruction. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2007;36:63–67. - PubMed
-
- Jadu FL, EWN The mystery of meal time swellings revealed. Oral Health. 2014;104:33–35.
-
- Strychowsky JE, Sommer DD, Gupta MK, Cohen N, Nahlieli O. Sialendoscopy for the management of obstructive salivary gland disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;138:541–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
