The Oxford Sleep Resistance test (OSLER) and the Multiple Unprepared Reaction Time Test (MURT) detect vigilance modifications in sleep apnea patients
- PMID: 25317088
- PMCID: PMC4173085
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.4104
The Oxford Sleep Resistance test (OSLER) and the Multiple Unprepared Reaction Time Test (MURT) detect vigilance modifications in sleep apnea patients
Abstract
Study objectives: The Oxford Sleep Resistance Test (OSLER) is a behavioral test that measures a subject's ability to maintain wakefulness and assesses daytime vigilance. The multiple unprepared reaction time (MURT) test measures a subject's reaction time in response to a series of visual or audible stimuli.
Methods: We recruited 34 healthy controls in order to determine the normative data for MURT. Then we evaluated modifications in OSLER and MURT values in 192 patients who were referred for suspicion of sleep apnea. We performed OSLER (three 40-min sessions) and MURT (two 10-min sessions) tests at baseline. Of 173 treated OSA patients, 29 professional drivers were retested within six months of treatment.
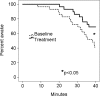
Results: MURT values above 250 ms can be considered abnormal. The OSLER error index (the number of all errors divided by the duration of the session in hours) correlated statistically significantly with sleep latency, MURT time, and ESS. Treatment improved OSLER sleep latency from 33 min 4 s to 36 min 48 s, OSLER error index from 66/h to 26/h, and MURT time from 278 ms to 224 ms; these differences were statistically significant.
Conclusions: OSLER and MURT tests are practical and reliable tools for measuring improvement in vigilance due to sleep apnea therapy in professional drivers.
Keywords: CPAP; alertness; excessive daytime sleepiness; reaction time; vigilance.
Figures

References
-
- Décary A, Rouleau I, Montplaisir J. Cognitive deficits associated with sleep apnea syndrome: a proposed neuropsychological test battery. Sleep. 2000;23:369–81. - PubMed
-
- Lim J, Dinges DF. Sleep deprivation and vigilant attention. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1129:305–22. - PubMed
-
- Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep. 1991;14:450–5. - PubMed
-
- Crawford MR, Bartlett DJ, Coughlin SR, et al. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure usage on sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnoea: real effects or expectation of benefit? Thorax. 2012;67:920–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

