Immunomodulatory effect of non-viable components of probiotic culture stimulated with heat-inactivated Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus on holoxenic mice
- PMID: 25317114
- PMCID: PMC4172693
- DOI: 10.3402/mehd.v25.23239
Immunomodulatory effect of non-viable components of probiotic culture stimulated with heat-inactivated Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus on holoxenic mice
Abstract
Background: Competition of probiotic bacteria with other species from the intestinal microbiota involves different mechanisms that occur regardless of probiotics' viability. The objective of this paper was to assess the cytokine serum levels in holoxenic mice after oral administration of non-viable components (NVC) of Enterococcus faecium probiotic culture stimulated with heat-inactivated Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus in comparison to NVC of unstimulated E. faecium probiotic culture.
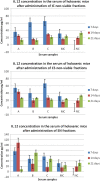
Methods: Probiotic E. faecium CMGb 16 culture, grown in the presence of heat-inactivated cultures of E. coli and B. cereus CMGB 102, was subsequently separated into supernatant (SN) and heat-inactivated cellular sediment (CS) fractions by centrifugation. Each NVC was orally administered to holoxenic mice (balb C mouse strain), in three doses, given at 24 hours. Blood samples were collected from the retinal artery, at 7, 14, and 21 days after the first administration of the NVC. The serum concentrations of IL-12 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) interleukins were assessed by ELISA method.
Results: After the oral administration of SN component obtained from the probiotic culture stimulated with heat-inactivated cultures of B. cereus CMGB 102 and E. coli O28, the serum concentrations of IL-12 were maintained higher in the samples collected at 7 and 14 days post-administration. No specific TNF-α profile could be established, depending on stimulated or non-stimulated probiotic culture, NVC fraction, or harvesting time.
Conclusion: The obtained results demonstrate that non-viable fractions of probiotic bacteria, stimulated by other bacterial species, could induce immunostimulatory effects mediated by cytokines and act, therefore, as immunological adjuvants.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecium; immunomodulation; interleukins; intestinal microbiota; non-viable components; probiotic.
Figures

References
-
- Adams CA. The probiotic paradox: live and dead cells are biological response modifiers. Nutr Res Rev. 2010;23:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Cocconier MH, Bernet MF, Kernéis S, Chauviére G, Fourniat J, Servin A. Inhibition of adhesion of enteroinvasive pathogens to human intestinal Caco-2 cells by Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LB decreases bacterial invasion. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993;110:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Lazar V. Quorum sensing in biofilms – how to destroy the bacterial citadels or their cohesion/power? Anaerobe. 2011;17:280–5. - PubMed
-
- Quadri LEN. Regulation of class II bacteriocin production by cell-cell signaling. J Microbiol. 2003;41:175–82.
-
- Moslehi Jenabian S, Gori K, Jespersen L. AI-2 signalling is induced by acidic shock in probiotic strains of Lactobacillus spp. Int J Food Microbiol. 2009;135:295–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
