Perspectives on the application of nanotechnology in photodynamic therapy for the treatment of melanoma
- PMID: 25317253
- PMCID: PMC4152551
- DOI: 10.3402/nano.v5.24381
Perspectives on the application of nanotechnology in photodynamic therapy for the treatment of melanoma
Abstract
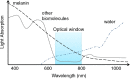
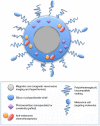
Malignant melanoma is the most aggressive form of skin cancer and has been traditionally considered difficult to treat. The worldwide incidence of melanoma has been increasing faster than any other type of cancer. Early detection, surgery, and adjuvant therapy enable improved outcomes; nonetheless, the prognosis of metastatic melanoma remains poor. Several therapies have been investigated for the treatment of melanoma; however, current treatment options for patients with metastatic disease are limited and non-curative in the majority of cases. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been proposed as a promising minimally invasive therapeutic procedure that employs three essential elements to induce cell death: a photosensitizer, light of a specific wavelength, and molecular oxygen. However, classical PDT has shown some drawbacks that limit its clinical application. In view of this, the use of nanotechnology has been considered since it provides many tools that can be applied to PDT to circumvent these limitations and bring new perspectives for the application of this therapy for different types of diseases. On that ground, this review focuses on the potential use of developing nanotechnologies able to bring significant benefits for anticancer PDT, aiming to reach higher efficacy and safety for patients with malignant melanoma.
Keywords: melanoma; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; photodynamic therapy; skin cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Baldelli FB, Webster CA, Moncrieff M, Sherwood V. The scope of nanoparticle therapies for future metastatic melanoma treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e22–32. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics 2014. CA: A Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Globocan 2012. Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.aspx [cited 15 January 2014].
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2013. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2013.
-
- Jhappan C, Noonan FP, Merlino G. Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:3099–112. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
